If you gave, or received a new cell phone, tablet, or notebook computer over the holidays, chances are that it included a USB Type-C® port and cable – even if you didn’t know it.
The first major, and obvious, advantage of USB-C® to the end-user is the fact that it’s a common standard physical interface that works across a wide range of different devices and manufacturers. This is a huge improvement in convenience and interoperability over how things were just a few years ago. It’s made even better by the fact that the connectors are omnidirectional – no more fumbling around or needing to visually check that you’ve got the cable / connector the right way around.
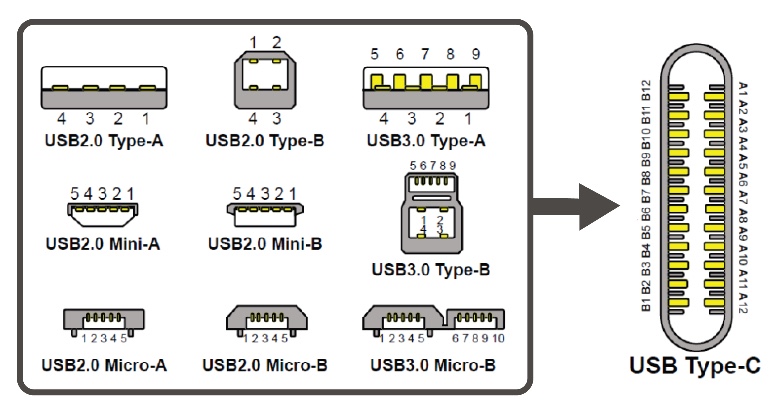
But while the Type-C connector is the visible front-end of the latest USB innovations, the real magic is what has been happening inside…
The Universal Serial Bus (USB) standard was first released in 1996 to standardize the connection of peripherals to personal computers – for low-speed devices such as a keyboard or a mouse with data speeds of 1.5Mbps. With the USB4 specification released in 2019, data speeds can reach up to 40Gbps (allowing you to transfer an entire movie from your phone to a computer in less than 1 minute) and is backwards compatible with USB 3.0 and USB 2.0.
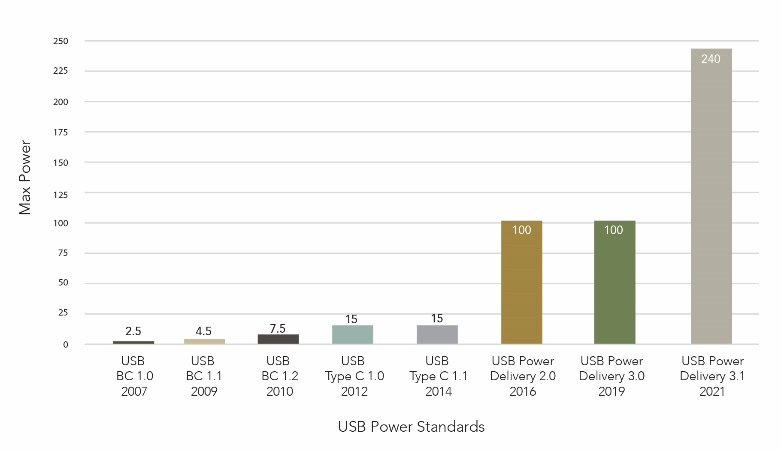
Along with these increases in power and data capabilities – and a connector that can conveniently handle them – has come a desire for shorter charging times for device batteries, as well as more efficient use of power. USB Power Delivery (PD) is a specification for handling higher power and allows a range of devices to fast-charge over a USB connection. The latest release of USB PD enables up to 240W of power with a full featured USB Type-C cable and port – providing one of the fastest charging protocols available on the market.
Programmable Power Supply (PPS) allows for stepwise changes in current and voltage – decreasing the conversion loss during charging, and thereby ensuring that charging is more efficient. Due to more efficient charging less heat is produced, which increases a battery’s lifespan, and decreases a device’s (and operator’s) heat signature.
USB PD now has become the de-facto charging protocol in the consumer market, and USB-C is becoming the universal cable / connector standard, due to its ability to supplying continuous high power plus blazing fast data transfer speeds. The end-user benefits of convenience, ease-of-use, and commonality are nothing to be underrated either.

The US military has issued USB-enabled tactical electronic devices through such programs as Nett Warrior, IVAS, and the upcoming Small Tactical Universal Battery (STUB) series. This trend is likely to increase as the US Army, US Marine Corps, USSOCOM and other government agencies look to modernize and upgrade their tactical electronics systems – while also looking to increase standardization and interoperability, while shortening development cycles and reducing overall program cost. Incorporating globally proven and industry standard technologies such as the USB specifications helps achieve these goals – as well as reducing the battery burden borne by the Warfighter.
Commercial mobile technology industry-leader Xentris Wireless created the EXO Charge division specifically to support such modernization efforts by developing rugged, lightweight, intuitive power solutions for the modern Warfighter. Learn more about EXO Charge at EXOcharge.com.

