In my 26 years in the US Navy, I came across some of the best Corpsman you could possibly imagine. Almost all have gone on to become doctors, not that that is a measure of anything. But the Rips the Doc Conza, Doc Henao, and Smiths of the SEAL teams would break their backs to make sure you were good to go. To all of them, Happy Birthday to all the Docs that patch us mortals up. The Rules for the Regulation of the Navy of the United Colonies of North America of 1775 contained only one article that directed the formation of Navy medicine. “A fitting area shall be set apart for sick or hurt men, to be removed with their hammocks and bedding when the surgeon shall advise that it is necessary: and members of the crew shall be designated to attend to and serve them, as well as to maintain the space clean,” according to Article 16.

Between 1775 and 1814, the period covered America’s first maritime conflicts, and little changed medical techniques and structure. Feeding and personal care of the non-combat wounded and injured were among the less dramatic obligations of caring for them. Untrained personnel was sure to bring down the minimal daily feed of porridge or “loblolly” to those in the medical section. On March 2, 1799, Congress passed an act that exacted the language of the Continental Congress’s medical department article 16 of 1775. As a result, enlisted medical personnel still lacked a title or job description. The term “loblolly lad” had been around for so long that it was adopted as an official title in the Navy Regulations of 1814. A new senior enlisted medical rate, surgeon’s steward, was established in the decades that followed. The phrase appeared in Navy pay charts for the first time in 1841; however, the new billet was only available on larger ships. The Navy Department issued an order on April 1, 1843, that allowed surgeon’s stewards to be attached aboard brigs and schooners. The relative relevance of medical Sailors was raised as a result of this. Surgeon’s stewards would be second only to the master-at-arms in seniority among the ship’s petty officers. With the tremendous rise in the Navy and the onset of the civil war in 1861, improvements and developments in the medical sector were bound to occur. On June 19, 1861, a Navy Department circular order gave the loblolly boy a new moniker.

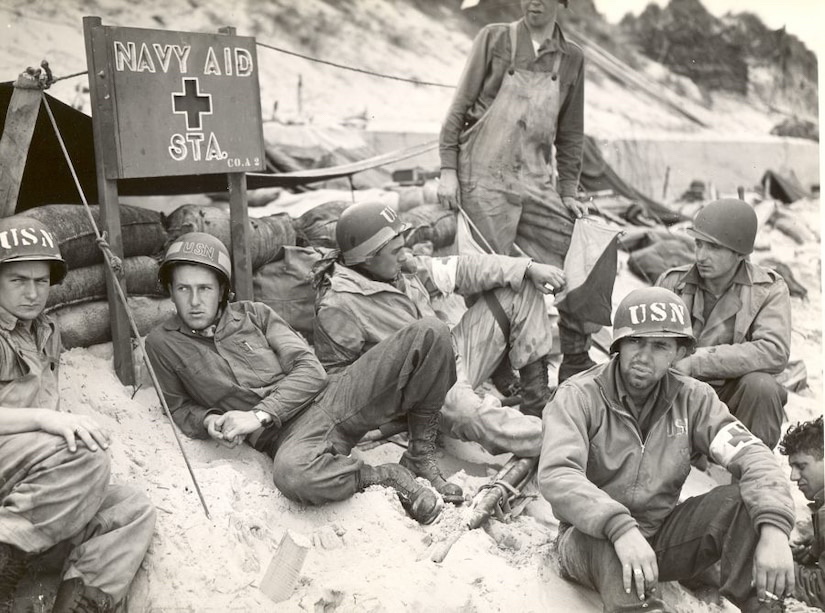
The United States Navy Hospital Corps was not formally created as a unit inside the Navy’s Medical Department until June 17, 1898. The Spanish-American War was looming on the horizon at the time, and the U.S. Navy and Marines needed a well-trained medical section. Since that time, Hospital Corpsmen have served with their fellow Sailors and Marines on every continent, on every warship, submarine, and ocean.
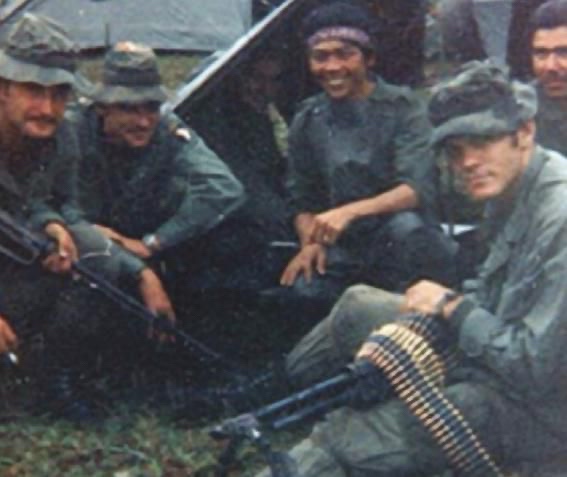
Modern hospital corpsmen can pursue additional training to become highly skilled medical specialists, specializing in areas such as laboratory technologists, dive medicine, or aerospace medicine.
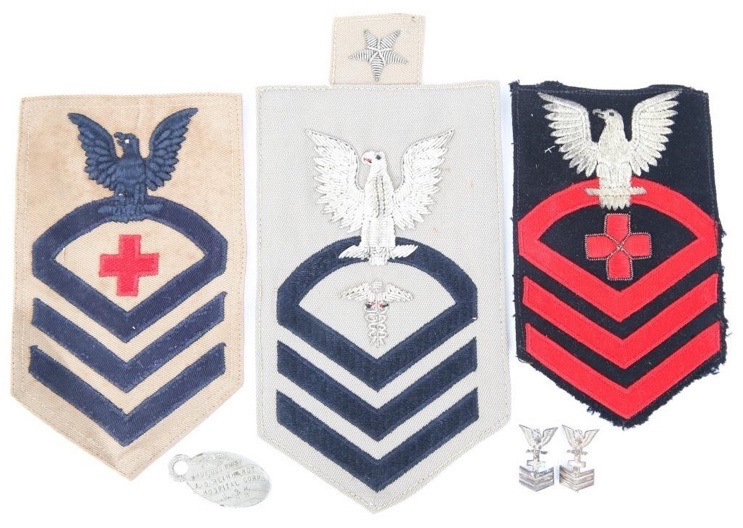
On August 29, 1916, Congress enacted the following significant change in the structure of the Hospital Corps. Hospital apprentices, second class and first class (both of whom wore a red cross on their sleeve), pharmacist’s mates, third, second, and first, and chief pharmacist’s mate would be the rates under this model. The two warrant officer grades of pharmacist and chief pharmacist would be included in the Hospital Corps’ officer contingent. The restructure would allow the Hospital Corps to grow by five times its current size. The Hospital Corps’ greatest manpower, diversity of duties, and example of sacrifice occurred during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, the ranks of this modest organization increased from about 4,000 at pre-war levels to over 132,000. This raise was necessary to meet new tasks that required new technology at new duty sites. The Hospital Corps’ reputation for efficacy and bravery would be cemented in the face of severe difficulty.

The Hospital Corps has a long history of courage and sacrifice. Hospital corpsmen have also responded to natural disasters, military mishaps, and peacetime emergencies. They’ve also kept their Sailors and Marines healthy by immunizing, practicing preventative care, and holding sick calls. 23,000 regular and 6,000 reserve Navy Hospital Corps troops serve globally. They operate in naval hospitals, clinics, ships, and submarines. Search-and-rescue missions and Seabee deployments. Not to mention their deployments with the Marine Corps and SEAL teams.
Corpsmen have always been responsible for shipmates’ health. Their endless acts of heroism, exposing themselves to risk to save lives, were essential. Because they cared about their shipmates, their bravery is notable.
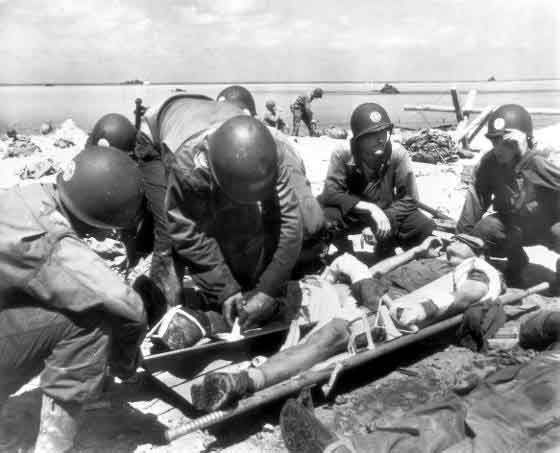

During the United States Navy Hospital Corps’ 124-year history, it has risen to become the most decorated rating in the U.S. military. 22 Medals of Honor, 179 Navy Crosses, 31 Navy Distinguished Service Medals, 959 Silver Stars, and almost 1,600 Bronze Stars with Vs. for heroism have been awarded to Corpsmen. In addition, 14 Naval Vessels have been named after Hospital Corpsmen, and other hospitals and clinics have been named after brave individuals who gave their lives in the service of our country and freedom.

