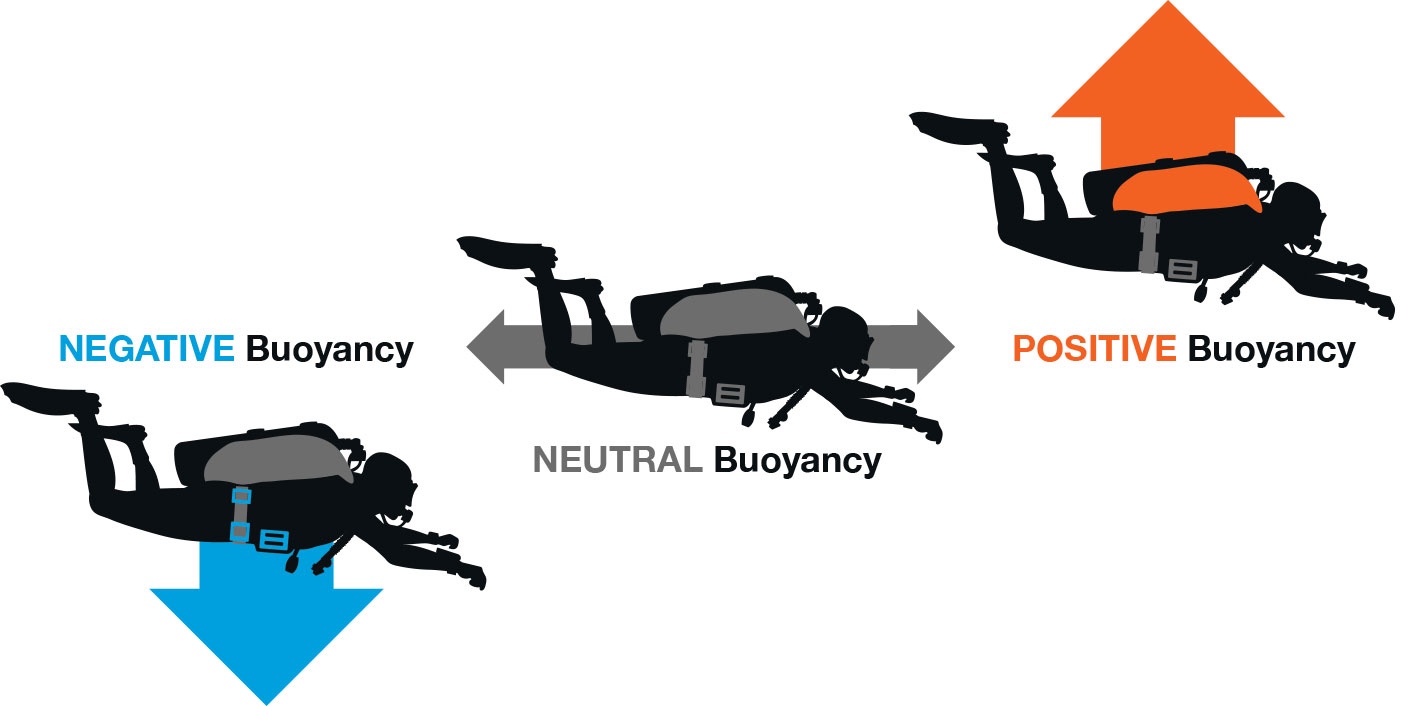
Buoyancy is key to a lot of things when diving. It helps make the dive easier in a lot of ways. When using a closed-circuit rig (CCR), it keeps you from rocketing to the surface, and it prevents you from dropping to the bottom when you stop to fix your gear or “Dräger” talk/ yelling at your dive buddy.
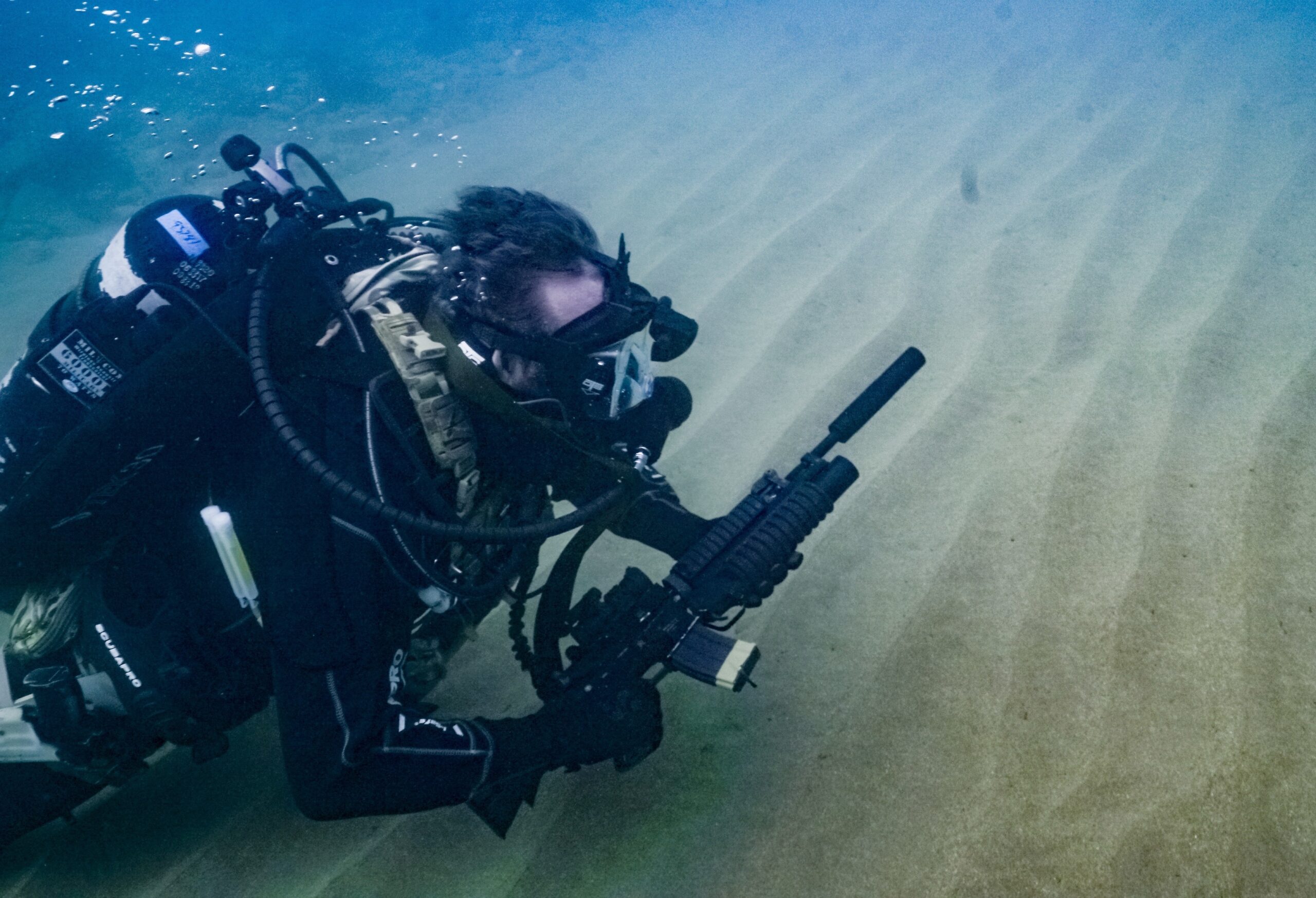

The keys to buoyancy are balance and breathing.
The two significant factors in achieving neutral buoyancy.
Wear the right amount of weight for the dive. This will differ depending on the thickness of your wetsuit/ drysuit and gear you are wearing, also water type fresh or salt.
Breathing slowly and evenly, so you do not have too much air in your breathing bag. If diving a CCR
Steps to help maintain buoyancy.
Pre-dive preparation.
Buoyancy control begins with pre-dive preparation as you pick what to wear for a dive. Double-check to make sure nothing has changed that could affect buoyancy. A new wetsuit is more buoyant than an older one and will need more weight. A new suit has more inherent buoyancy at first because diving, especially deep diving, bursts the tiny bubbles in the suit over time. Make sure you look at any new gear compared to the old version. Equipment is constantly evolving and updated with new buckles or martial, so when you switch from old to new, make sure you know the buoyancy with the new stuff. Check the weights on a scale; often, there is variation between claimed and actual weight. If diving open circuit, remember cylinders are negatively buoyant when full and less negative when empty.

Do a buoyancy check.
Here is the best way to do a proper buoyancy check. With your lungs half-full, you should float at eye level with no air in your BCD. If you are diving open circuit, remember the average cylinder loses about 5 pounds as it empties. So, you might have to add about 5 pounds to your weight if you have done your buoyancy check with a full tank.
Keep a log
Keep a log of what gear you have worn, the temperature, and the type of water (salt/fresh /brackish). What equipment you used, how much lead you carried, your body weight, and whether you seemed too heavy or light. Knowing the weight of the gear that you used on the dive will help. Make sure you understand that if you are going to remove something during the dive, you need to account for that on the return trip home. If you plan by recording in training what you used, it will help when you have to do it the next time.

Saltwater VS Freshwater.
If most of your driving is done in the ocean, ballast calculations should be done for saltwater. Jumping in the pool to check your ballast will get you close, but it won’t be 100% correct. If you switch back and forth, you’ll need to adjust your ballast. Be prepared to add weight if needed sometimes, it’s nice to have a weight belt with extra pouches just in case, or maybe just an empty pouch on a gear belt will help. But still, try and keep the weight evenly distributed.
Buoyancy, Trim, Position, and Breathing
The secret to buoyancy control begins with fine-tuning your weighting. How much lead do you put into your pouches or have on your weight belt? If you carry just the right amount of weight, you will only have to put a little air in your BCD. That means less drag and more efficient finning. Less BC inflation also means minor buoyancy shift with depth, so you’ll have to make fewer adjustments. There are many tricks, but buoyancy control is a fundamental skill. Precise control of your buoyancy is what enables you to hover motionless and fin through the water at any depth. It would be best not to use your hands and not stir up mud or silt from the bottom by always moving your feet. In addition to using the right amount of weight, make sure you are correctly balanced to optimize your position underwater.
Keeping a more horizontal position makes you more hydrodynamic. Distribute the weight as uniformly as possible from side to side; you should never notice that you put more weight on one side while driving. It would help if you also considered the weight of your dive gear and any other additional gear you might be wearing. I.e., gun belt or special equipment. Make sure it is balanced on your body, and it doesn’t shift when you are diving. The lower you wear your dive rig can cause a tendency to push the diver forward (upside down) in the water, so the placement of weight towards the back can help reverse this position, especially on the surface. Make sure any dive weight you put on can be easily removed in an emergency.
Besides ballast weight, the factors that affect your buoyancy are BC inflation, your trim, exposure suit, depth, and breathing control. Your ballast weight and your trim are the only two factors that, once you’ve selected them, stay put. Ballast is the amount of weight it takes to keep you neutral in the water. Trim is about the position of your body weight relative to the position of your weight. Sometimes when diving a rebreather, you can tape lead washers on it to help with your trip.
There is one more thing to understand that will help with your buoyancy. It is controlling your breathing. Make sure you maintain proper breathing. Take relaxed breaths. This allows you to maintain control over your buoyancy.
To determine the amount of weight you need, you can take your body weight, the diving suit you will use, the weight of your equipment, and the environment you are diving in salt or freshwater. If you use about 10 percent of your body weight, that is a good starting point for a full 5 mm or more and for a 3 mm suit, use 5 percent of your body weight.

Drysuits and thick neoprene suits require more ballast to counteract the increased buoyancy of those suits compared to the thinnest. Body composition (the muscular density, for example) will also influence the necessary weight. Remember, fat floats, muscle sinks.
Remember to calculate everything you will use and wear on your dive if you are doing a long drive and plan to leave or remove something halfway thru your dive. Say conducting a ship attack, and you are taking limpets off. Plan for the whole dive, not just the start when you will be at your heaviest; plan if you are carrying something that you plan to leave behind, how will that affect your extraction. To check your buoyancy, get into the water deep enough to stay in an upright position without treading and releasing all air from the vest. Inhale, normally, the surface of the water must be at the level of your eyes. When you exhale, you should sink until the water covers your head and inhale again. You should emerge once again until the level of the eyes. Adjust your weight in small increments, about 1 pound at a time. You can use a weight with a snap link or just some weight with some 550 cord on it. Make sure you don’t just put all the weight you are adding to one side. Try and use this time to even yourself out and set your trim also. I have also seen people tap lead washers to the front of their rebreather to help even them out. The rule of thumb is never add more than 10Lbs. that can’t be released.

Once you get your ballast weight and trim dialed in, you will be ahead of about 75% of all divers toward perfect buoyancy control. Now you can fine-tune your BC inflation to compensate for the very predictable changes due to breathing down your tank and changing depth.
Lastly, there are advanced classes that you can take that focus on advanced skills like this. This may seem like a lot of work, but it will help make diving a lot better and make you more efficient at your job.

