No matter what you are doing, you should have as many tools stacked in your favor or in your toolbox as you can to help back up your gauges and also make it easier on you. If all else fails, you can use your depth gauge and the depth around the target to find out where you are and where you need to go. It can be as simple as swimming with a reef on one side on the way out and the other on the way back.
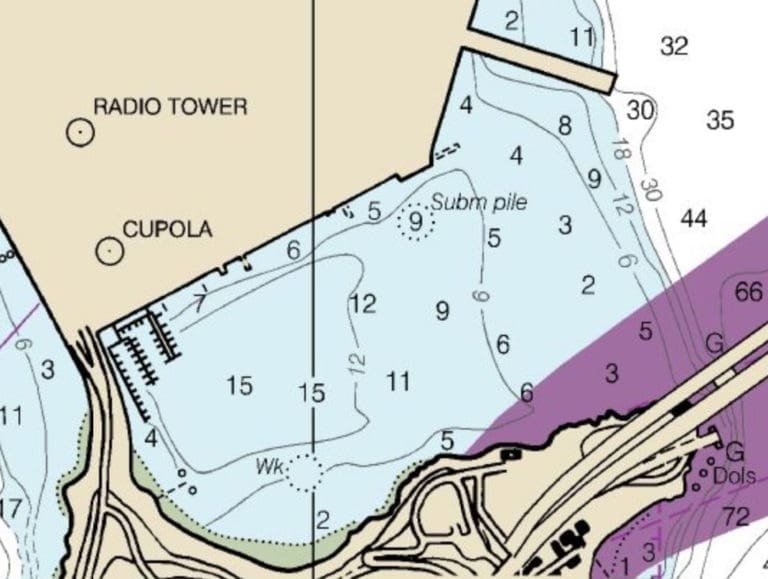
Contour lines are used on charts and maps to represent the shape of the land and the ocean’s bottom. By using these lines, you can get a three-dimensional picture of what the bottom should look like. It is hard to overstate the importance of contours when it comes to navigating. This can also be said about using the background from the water looking towards the land as a form of contour navigation. Knowing things that can help you tell where you are, like the piers’ compass heading, what direction does it go. What will the background look like behind your target, even the silhouette of the buildings? The movement of the moon will be in front or behind the target. If you have to use contour navigation, what would that look like?

You can also use the direction of the waves to find your way back to shore (along shorelines, waves will usually move in the direction of the shore) or using the contours of the bottom to make sure you’re moving in the right direction.
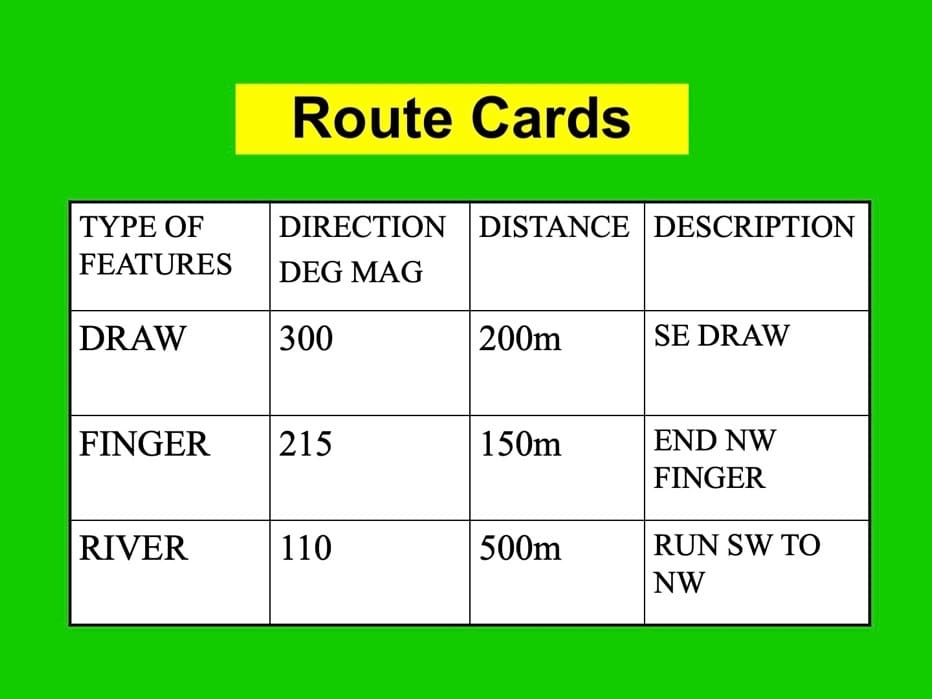
Good navigation begins long before you get into the water. You and your dive buddy should do a target and map/chart study to become very familiar with the target and surrounding area. Valuable information about the site, its features, depths, currents, moon phases, and surrounding features will help build a good dive plan. Discuss constitutes for your profile and which safety precautions you’ll take and agree on a primary route—lastly, walking thru what the dive will be like and what to do if you are lost or come up to different points.
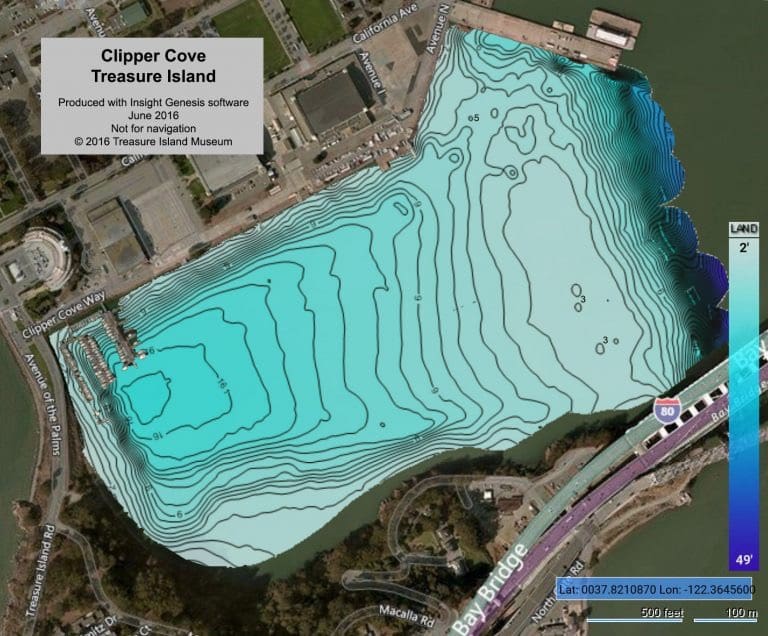

Search for landmarks so you can reset yourself. Distinct underwater features can be found, including coral formations, objects, or differences in the bottom contour. Make sure to note any insights that stand out, and make sure to document every detail. Use what you have learned from the harbor’s contour or where you are diving as you pass through one of the following thresholds: 10 feet, 15 feet, or 20 feet, also. How is the bottom running? Remember to look for landmarks also along your dive route. Follow the light, look for lights, and even the moon if it is out. Check the angle of the moon at the start of your dive or if it hasn’t come up yet, which way will it raise and try to confirm this when you begin your descent. Before you go under, if you are turtle backing, you can use the moon or stars to help you navigate, so you don’t have to look at your navigation board continually. Before I went to BUD’S, I was a boat guy, and I learned to use the stars and moon to help me navigate, many times in the water and on land; this helped because I didn’t always have to be taking my compass out to make sure I was going the right way.

Depending on your dive computer, some like the SCUBAPRO Galileo 2 (G2) allows you to store pictures, so you can store a route card or a picture of the bottom, you can look at what the bottom should be looking like or have a picture of other things around the target to help. The G2 can also be used as a navigation/ attack board. Lastly, don’t be afraid to slow down a little. There is no reason to rush to be further lost than you are. Stop, and come up with a plan and then work that plan.



Excellent post and would go a long way with land nav.
Thanks. I took a lot of it from old land nav courses. The two are basically the same thing. Thanks again
Question please!
Your table uses meters & meters.
Easier to standardize on metric: mils & meters?
Normally all navigation for the military is metric, but that said all but when done only below the water. It’s yards and feet. Well that is the US military .
Thanks.
I’m not going to ask why…