Last week’s NDIA Armaments Forum ended with a briefing by Naval Surface Warfare Center – Crane, of what is this year’s most applicable topic, for both the US military as well as manufacturers of commercial AR variants. Last year Crane unveiled their findings regarding KeyMod vs M-Lok. This year it’s the performance of a mid-gas system on an M4 carbine.

NSWC-Crane, or Crane as it is commonly known, is located in rural Indiana. In addition to providing a wide range of acquisition services for the US Navy, they are also responsible for the test, evaluation, procurement and life-cycle management of SOF weapons. It’s in this role that they evaluated the mid-length gas system for United States Army Special Operations Command M4A1 carbines.
Gas System History
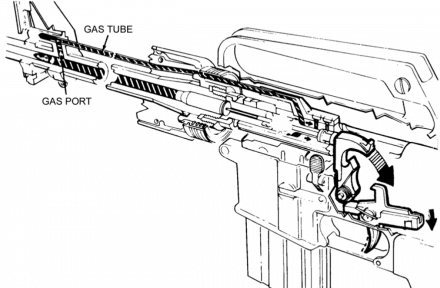
The M16 Rifle and variants use a 20” barrel and gas system. This rifle length gas system uses a gas tube 15” in length with gas port at 13”. The well distance is approximately 7”.
When the M4 was developed, research concluded the Army should utilize a 14.5” barrel for the M4 & M4A1 carbines
This necessitated redesign of the M16 gas system because a 14.5” barrel with a rifle length gas system had only 1.3” dwell distance. Consequently, they gas port was moved to 7.8” from bolt face on M4 offering 6.7” dwell distance.
This decrease in distance from the bolt face to the gas port resulted in an increased port pressure in the M4 carbine when compared to M16 rifle. The port pressure of the M4 at 7.8” from the bolt face is 17,000 psi, while port pressure at 13” from bolt face of the M16 is 10,000 psi.
Mid-Gas Testing included:
– Endurance
– Reliability
– Precision
– Muzzle Velocity
– Terminal Velocity (@100 yards)
– Bolt Speed
– Low Temperature (-60F)
– High Temperature (160F)
– Barrel Erosion
However, the briefing did not address every area of testing.
Endurance & Reliability
So far, Crane has put 30,400 rounds of M855A1 through three M4A1s equipped with 14.5″ cold hammer forged barrels and a mid-gas system with a gas block approximately 9.8″ from the bolt face.
They stated SOF M4A1s normally start to see accuracy degradation at around 6,000 rounds. But during testing of the mid-gas system, they’d hit 12,600 and still hadn’t seen any changes.
They also have only broken one bolt so far in testing, although I don’t think they’re ready to attribute the improved bolt performance to the mid-gas system.
The Crane team will finish testing up with 34,000 rounds per upper. It’s not that they don’t think the barrels can’t take more, but rather that they had to use the same lot of M855A1 to satisfy the accuracy portions of testing.
USSOCOM Accuracy Testing & Protocol
With this mid-gas system they are getting 5 MOA groups while the standard is 7 MOA. One of the three uppers was shooting 1 MOA, except for the tenth round which was still within limits.
Interestingly, USSOCOM tests accuracy differently than most others. They fire 10 rounds suppressed and another 10 rounds unsuppressed. They measure the extremes of the spread of impacts, rather than their closest points. Then, they do it again two more times and average the results to determine accuracy.
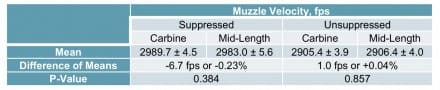
Muzzle Velocity
These measurements are averaged and validate what we know about the use of suppressors increasing muzzle velocity.
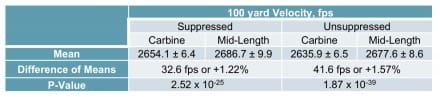
Terminal Velocity
The velocity at 100 yards for mid-length weapons is 32.6 fps or 1.2%, higher for suppressed fire and 41.7 fps or 1.6%, higher for unsuppressed fire.
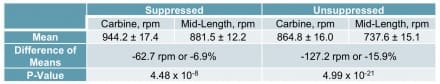
Cyclic Rate
Mid-length cyclic rate of automatic fire was 62.7 rounds per minute (rpm), or 7%, lower than carbine-length for suppressed fire and 127.2 rpm, or 16%, lower for unsuppressed fire.
Temperature High & Low
960 rounds were fired at 160F for Reliability at High Temp and another at -60F for Reliability at Low Temp.
For carbine-length weapons, 5 out of 65 malfunctions occurred during high temperature testing. For mid-length weapons, 1 out of 30 malfunctions occurred during high temperature testing. For high temperature testing, carbine-length weapons had 576.0 mean rounds between failures (MRBF) compared to 836.1 MRBF for ambient temperature testing and mid-length weapons had 2800 MRBF compared to 1993.8 MRBF for ambient temperature testing.
For carbine-length weapons, 27 out of 65 malfunctions occurred during low temperature testing. For mid-length weapons, 16 out of 30 malfunctions occurred during low temperature testing. For low temperature testing, carbine-length weapons had 333.3 mean rounds between failures (MRBF) compared to 836.1 MRBF for ambient temperature testing and mid-length weapons had 562.5 MRBF compared to 1993.8 MRBF for ambient temperature testing. Approximately half of the total malfunctions recorded for both carbine-length and mid-length weapons occurred during low temperature testing, so the relative rate of malfunctions between carbine-length and mid-length remained similar to that of ambient temperature testing.
Conclusion
Although testing to 34,000 rounds isn’t yet complete, the conclusion is simple. Use of a mid-gas system significantly extends the life of the overall weapon system. It also offers increased performance over a carbine-length gas system.
Implications
This information is particularly important for the US Air Force’s Improved Modular Rifle – Blue program which templates off of upper receiver group improvements adopted by USASOC (Brownells is offering a similar package for reference). While USASOC will upgrade up to 15,000 carbines, the AF wants to modify around 50,000 guns. That could be enough to force a major Technical Data Package update applicable to all services and creation of a GOTS upgrade for all M4s, regardless of service.
This government testing also validates what many commercial vendors have been offering for years.