WRIGHT-PATTERSON AIR FORCE BASE, OHIO (AFRL) – Longtime Air Force Research Laboratory, or AFRL, industry partner AlphaMicron Inc., is utilizing a 2021 Ohio Federal Research Network, or OFRN, funding award to expand the capability of its patented guest host liquid crystal technology, called e-Tint, to electronically dimmable protective eyewear for the Department of the Air Force, or DAF, Department of Defense and commercial markets.
The $1.35 million award, comprised of $900,000 from the state of Ohio and a $450,000 AlphaMicron, or AMI, cost share, enables AMI to apply emergent fundamental research toward the expansion of its e-Tint technology for the development of advanced sun protection devices for pilots and special warriors, as well as specialized laser protection film for civilian and military eyewear, said Principal Electronics Engineer Dr. Darrel G. Hopper in the Airman Systems Directorate of AFRL’s 711th Human Performance Wing.
In its persistent mission to mature its technology and create advanced applications, AFRL has partnered with AMI — a global leader in liquid crystal-based light reactive technologies — since its founding in December 1996 as a spinoff of Kent State University’s Liquid Crystal Institute, Hopper said.
“Most recently, AMI was a performer under the 2018 Electronically Dimmable Eye Protection Devices Small-Business Technology Transfer Research (STTR) program sponsored by the Airman Systems Directorate,” Hopper said. “During the 2020-2022 Phase II award, AMI partnered with Bowling Green University, Kent State University and Miami University to develop next-generation electronically dimmable eye protection devices enabling them to work toward the 70% transmission window needed for current and future DAF applications.”

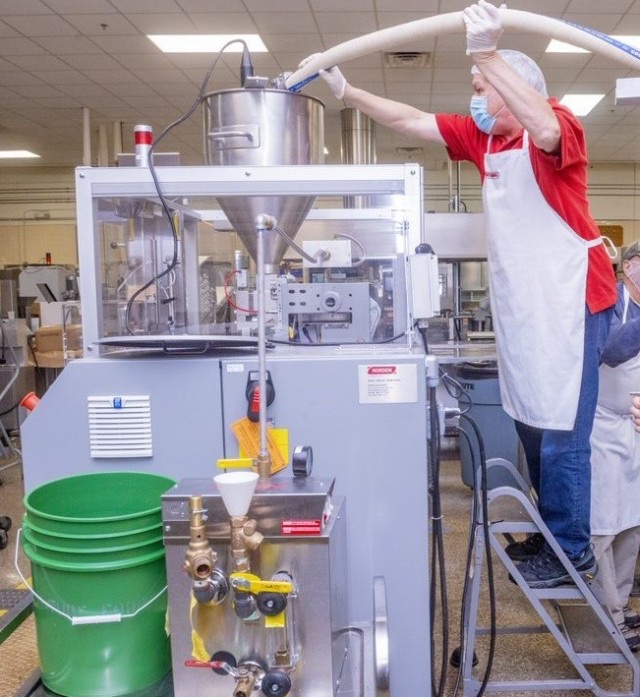
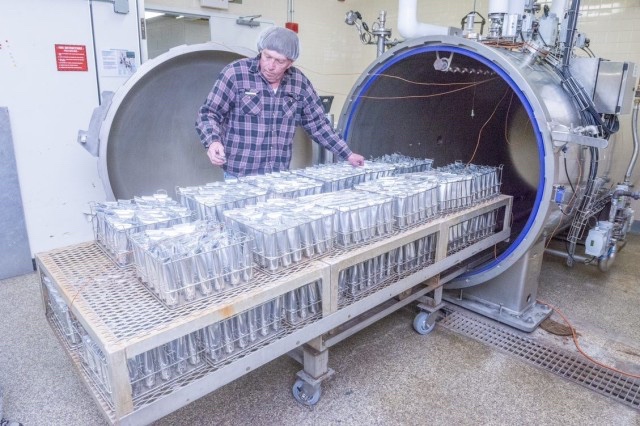
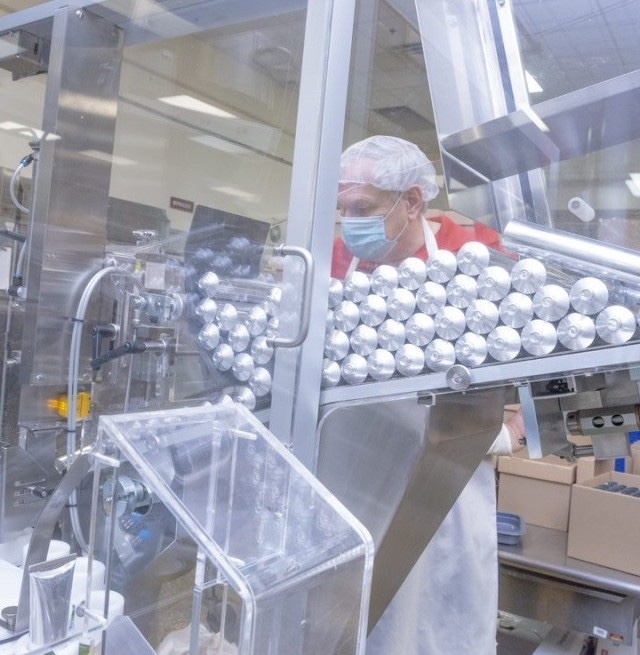
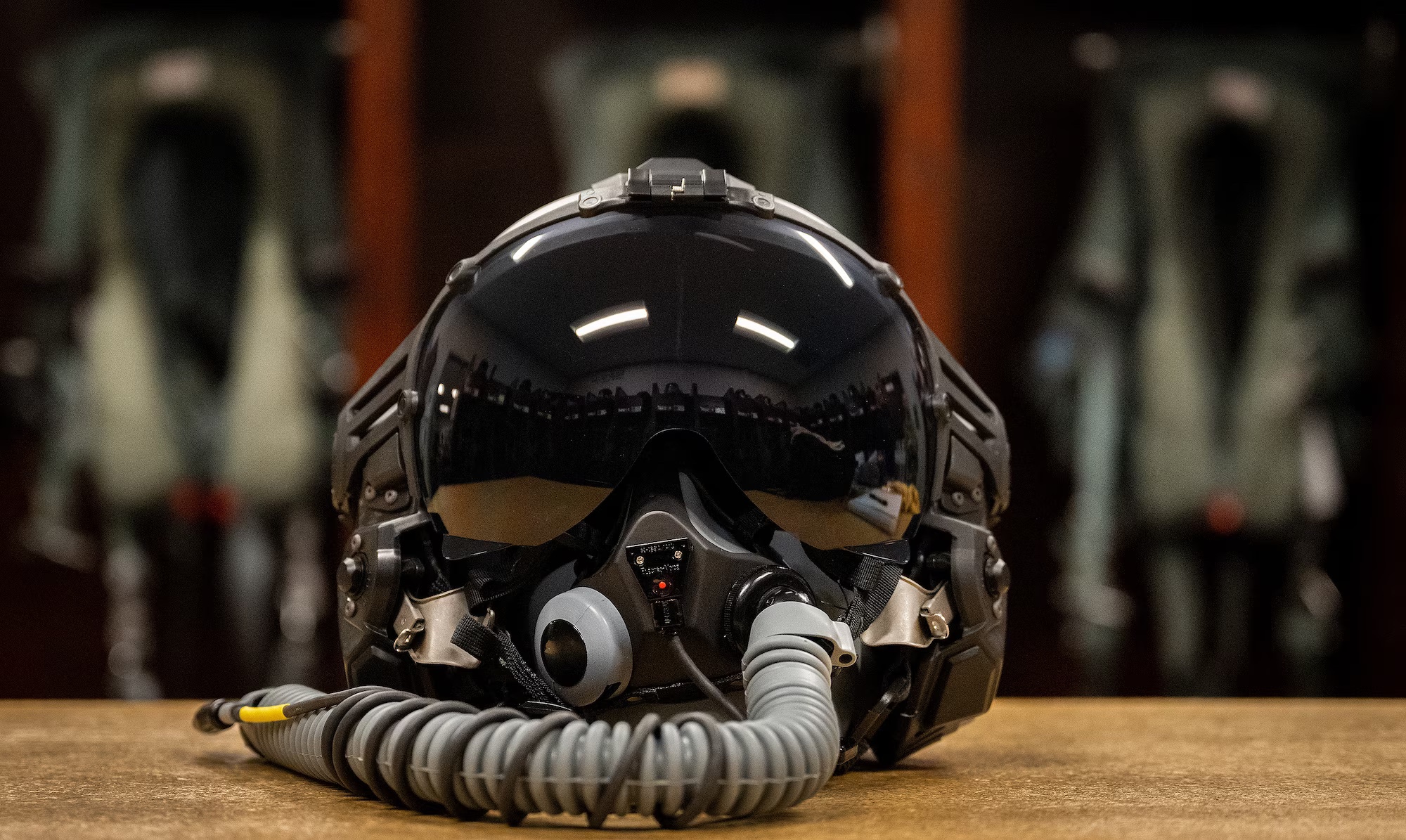
The image depicts AlphaMicron Inc., or AMI’s prototype progression over the course of 20 years. AMI’s first dimming proof of principle prototype from 1997 was eventually integrated into a Full Complex Curvature Helmet F-35 Visor prototype for the U.S. Department of the Air Force in 2017 to help mitigate pilots’ difficulties managing light transmission during flight. The initial collaboration between AFRL and AMI resulted in the creation of e-Tint, an electronic tint-on-demand liquid crystal technology that can be applied to flexible plastic substrates, such as pilot visors, instead of traditional glass. e-Tint switches from clear to dark faster than an eye can blink — about 0.1 of a second— and is fail-safe in a power outage. This technology was used to create the world’s first electronic switchable eyewear which was field tested by the U.S. Army and is now being issued to soldiers through the Approved Protective Eyewear List.? In addition to current applications, the technology is being developed for augmented reality applications and see-through displays, where simultaneously controlling ambient and display light is important, said AMI’s Chief Technology Officer and Chief Executive Officer Dr. Bahman Taheri.(U.S. Air Force photo)
The AFRL-sponsored 2018 STTR award expedited AMI’s process of qualifying and applying for the OFRN funding, as AMI was able to sustain the same academic partnerships it had developed under the previous effort, Hopper said.
AMI’s OFRN effort was one of five selected in the OFRN round five: Sustaining Ohio’s Aeronautical Readiness and Innovation in the Next Generation, or SOARING, Opportunity Announcement. According to its website, OFRN awards funding for projects that help expand Ohio’s research capabilities and grow its workforce in the areas of defense, aerospace, energy and health.
“AFRL’s history with AlphaMicron is long and rich,” said Personal Protection Direction Lead Dr. Matthew Lange in AFRL’s Materials and Manufacturing Directorate. “This OFRN funding is so important because it is what gets this kind of technology done. It’s enabling the continuation of solutions that are relevant to DOD needs.”
The storied relationship between AFRL and AMI led to the development of foundational optical technology with numerous commercial and military applications, said Dr. Richard Vaia, chief scientist, AFRL’s Materials and Manufacturing Directorate.
“This ensures critical suppliers have multiple revenues for pervasive aspects of critical technology for future DAF systems,” Vaia said.
AMI’s collaboration with the DAF dates back to its first Small Business Innovation Research, or SBIR, award in 1997 under the Variable Transmittance Visor program, Hopper said.
Prototypes produced under this first agreement eventually led to future collaborations with AFRL.
In 1997, AFRL partnered with AMI to address light management issues in fighter pilot helmets; researchers were challenged to develop variable-tint visors that would enable pilots to see clearly in flight, despite fluctuating lighting conditions. When pilots encountered sudden washes of intense sunlight mid-flight, they struggled to read and track the data on their aircraft-mounted and head-mounted displays, Hopper said.
“There was a need for some way of controlling visor tint, as it was affected by the transmission of light when the pilots would go above or below the clouds,” said Chief Executive Officer and Chief Technology Officer Dr. Bahman Taheri, who co-founded AMI with two other colleagues in 1996. “This was a safety hindrance. So AFRL asked us to join them to find a solution [based on the then-new guest host liquid crystal technology].”
AFRL and NASA have been working on solving this problem since the 1970s, Hopper said. It has taken the industry 20 years to realize the need for this type of technology for near eye applications. This need has accelerated with the recent emphasis on augmented reality glasses where displayed image contrast can be washed out because of the background ambient lighting conditions.
The initial collaboration between AFRL and AMI resulted in the creation of e-Tint, an electronic tint-on-demand liquid crystal technology that ultimately helped mitigate the pilots’ difficulties managing light transmission during flight. According to AMI’s website, e-Tint switches from clear to dark faster than an eye can blink — about 0.1 of a second— and is fail-safe in a power outage. Notably, the technology can be applied to flexible plastic substrates, or surfaces, instead of traditional glass, to benefit Airmen and Guardians.
“The Air Force was very specific about what it wanted,” Taheri said. “There were all of these boxes we needed to check. And one of them was they wanted to be able to encapsulate the layer of liquid crystal — which is very thin, 6 microns, so about one-tenth of the diameter of a human hair — between plastic. Glass is brittle and flat, not flexible and curved. If you drop it, it breaks. Flexible plastic substrates do not shatter, and they’re lightweight.”
All of these qualities make plastic desirable to glass when it comes to developing agile solutions for pilot eyewear, Taheri said, but the task of translating the liquid crystal technology to flexible plastic substrates was not without its challenges.
“Precisely because it’s flexible, it can be difficult to apply that thin layer of liquid crystal between two pieces of plastic and maintain uniformity,” Taheri said.
Around 2010, AFRL Chief Technologist Dr. Timothy Bunning led efforts within the Materials and Manufacturing Directorate to bring AMI on board to partner with members of his research team in what was then called the Functional Materials Division. Bunning’s group was working on expanding in-house liquid crystal research and develop resilience technologies relating to laser and flash eye protection. Bunning, who served at the time as division chief and, later, as the directorate’s chief scientist, assembled a research team that included Lange, Dr. Michael McConney and Dr. Timothy White, among others.
Together, the AFRL and AMI researchers sought to translate AMI’s preexisting e-Tint technology on flexible plastic substrates to variable-tint visors for DAF pilots.
“Our efforts with AMI were very fruitful,” Bunning said. “In AFRL, we are list-makers, we are very structured, we are always proactively pushing the bounds of the research. Our collaboration [with AMI] allowed us to combine efforts to reduce the risk of these new technologies, and it also led to some high-end publications in prominent scientific journals.”
White, who has since transitioned out of AFRL to take up a professorship in the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering at the University of Colorado-Boulder, said the vibrant partnership between his research team and AMI successfully resulted in the pursuit of both near- and far-term laser and flash eyewear protection solutions.
“Alpha Micron was and continues to be an incredible partner for the DOD to work with,” White said.
Taheri said his various collaborations with AFRL have opened doors to do more of what he genuinely enjoys.
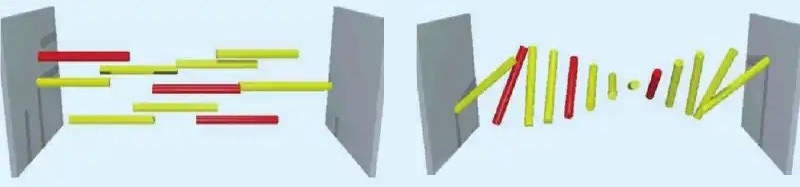
The graphic illustrates how reorienting liquid crystal (yellow) causes dichroic dye (red) to reorient along with it, which changes the transmission of light. In 1997, the U.S. Department of the Air Force identified a need for controlling visor tint in pilot eyewear. Visor tint was affected by light transmission when pilots would go above or below the clouds, as sudden washes of intense sunlight mid-flight impacted their ability to read and track the data on their aircraft-mounted and head-mounted displays. To address this safety issue, AFRL partnered with Kent State University-based AlphaMicron Inc., or AMI, a global leader in liquid crystal technology, to find a solution based on AMI’s proprietary polarizer-free, guest-host liquid crystal system known as e-Tint. AMI’s Chief Technology Officer and Chief Executive Officer Dr. Bahman Taheri likens this system to a molecular version of a Venetian blind. (Courtesy photo / AlphaMicron Inc.)
“Working with AFRL gave and continues to give me a glimpse into what the future of eyewear is going to be,” Taheri said. “This helped AMI create the e-Tint technology for head-mounted displays, and ambient and intense light management for the warfighter. It is the reason that AMI’s CTRL Eyewear is now the only electronic military grade eyewear in the Army’s Authorized Protective Eyewear List (APEL). It took 25 years for the consumer electronics companies working on advanced electronic AR glasses to realize this need.”
Most recently, AMI has set its sights on expanding its technologies beyond near eye applications to the commercial automotive and architectural sectors. The company plans to leverage its preexisting connections to major automotive Tier 1 companies to apply electronically dimmable technology to replace electrochromic mirrors in electric cars, and to integrate sunroofs with switchable glazing technology. These measures will help maintain more consistent temperature control and extend battery life in electric vehicles.
“With the advent of electric cars, what [the auto industry] is really starting to want is this switchable glazing that can be applied to the glazing in the vehicle to stop the car from heating up when it’s parked,” Taheri said. “Heat can be a big drain on an electric car battery when you are trying to cool it down and having a sunroof that ‘switches’ makes a big difference there.”
Taheri said he credits his company’s collaboration with AFRL for giving AMI a head start in this field.
“Because of our interaction with AFRL, AMI is now the main supplier of the much-needed dimming element to many of these top tier companies,” Taheri said. “In that same tone, I genuinely believe that the work currently being performed for the AFRL [with Dr. Lange and his team] is also decades ahead of its time. I have no doubt that it will be the solution to some of the problems not yet realized in the consumer market.”
The company’s commercial expansion can only mean good things for the future of AFRL, Lange said, as the development of any new industry technology can provide fresh avenues for meeting DOD supply chain needs.
“It’s so important to continue to support our industrial base at all levels in order for them to be successful,” Lange said.
Hopper, Lange and Taheri said they look forward to future AFRL collaborations.
“Some of the coolest projects always come from the Air Force,” Taheri said. “My team always wants to gather in on those because they know there’s going to be a tough problem to solve.”
-Gail Forbes, Air Force Research Laboratory













































































































































