ROBINS AIR FORCE BASE, Ga. (AFNS) —
Since its first flight Aug. 23, 1954, the C-130 Herculeshas proven to be one of the most versatile and active aircraft in the Air Force’s fleet, having carried troops and supplies from the tundra of Antarctica, to the deserts of the Middle East, to the tropical islands of the Pacific, and nearly everywhere in between.
Robins Air Force Base, host of the C-130 70th Anniversary celebration, has played a key role in keeping the C-130 fleet not just flying, but equipped with the technology and modernizations that make it a critical component of the contemporary Air Force fleet.

“It’s the greatest airplane ever built, and it’s stained honorably with American blood, sweat and tears,” said Gen. Mike Minihan, commander of Air Mobility Command. “That airplane is a monument to everyone that flies, fixes, and supports it … From the assembly line, to the flight line, to the depot line, it’s the hands that touch it that make it so powerful.”
The Warner Robins Air Logistics Complex at Robins AFB is the central hub for depot maintenance and modernization of the C-130. With 12 different C-130 models spread across seven major commands and the Air National Guard, totaling 436 aircraft in the Air Force fleet, effective and efficient maintenance is vital to keeping the mission running – especially in an era of Great Power Competition.

“We’re the best at what we do here,” said Ben Stuart, 560th Aircraft Maintenance Squadron director of operations. “The first flight was in 1954, and we’ve been doing depot maintenance on C-130s at Robins since 1964.

We’ve got mission partners with the program office, engineering, the Defense Logistics Agency and Lockheed Martin,” Stuart continued. “That combination is what makes us the best in the business, and we have been doing it for 60 years. Nobody else in the world does the repair and overhaul work that we do here at Robins.”

Around 50 of the aircraft come through each year for maintenance, to include planned depot maintenance, unplanned depot-level maintenance like battle damage repair, and modifications.
While Robins does significant C-130 work on the installation, the scope of its mission does not stop at the gates.
The Air Force Life Cycle Management Center’s C-130 engineering team regularly receives Engineering Technical Assistance Requests, where in-unit maintenance teams run into issues they are not able to solve on station. In 2023, the AFLCMC team received almost 3,500 ETARs, many of which resulted in the aircraft being grounded. In responding to these, Robins AFB coordinates with the home units to find a solution. When needed, engineers will deploy to the aircraft’s location to resolve the issue, keeping the global C-130 fleet flying and active.
As the Air Force calls on its members to reoptimize for Great Power Competition, the C-130 is being prepared for its next chapter. The call for reoptimization, the emphasis on Agile Combat Employment and the challenges of the Pacific theater mean that the C-130 will need to continue evolving.
“To survive and operate in that environment, it will absolutely be on the backs of our C-130s,” said Michael Beasley, the Mobility Directorate C-130 Hercules division senior materiel leader and retired maintenance officer.

According to Beasley, one of the biggest challenges in reoptimizing for GPC is the logistical hurdles that come with the change in area of responsibility.
Beasley spoke on how flights in the Middle East were often short range, only lasting a few hours, with less concern for fuel and range management.
Moving to operations in the Pacific, with major hubs often thousands of miles apart with nothing but ocean in between, that sentiment has changed.
“In the past we never had to worry about that, right? We’re just flying from Ramstein Air Base, (Germany), down to Iraq,” Beasley said. “We didn’t have to worry about that long term, or that margin at the end of the flight that says, ‘Man, I need to squeeze just another hour and a half out of this airplane.’ GPC has us thinking about how we can do that.”
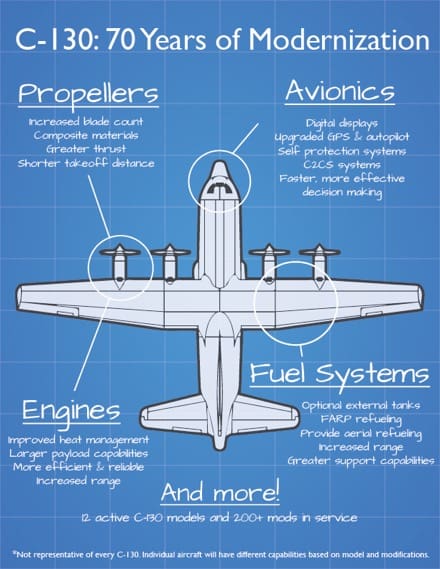
From increases in engine power and efficiency, to new propellor technologies and weight reduction efforts, the modernization efforts of the C-130 are a series of upgrades that not only provide individual benefit but work in tandem to make the aircraft as effective as possible.
“We’re trying to squeeze out every bit of performance out of this airplane we can, because we know that we’re probably the bedrock of that ACE concept,” Beasley said. “Once we get everything in theater and we’re in the battle, what’s going to keep that battle alive are the C-130 tactical transports, getting that stuff from island to island.”
The C-130 has also seen a number of avionics upgrades aimed at increasing effectiveness in a connectivity-contested environment.

Two technologies being utilized are the Real-Time in Cockpit and Dynamic Retasking Capability systems. These allow the C-130 to receive key information from command-and-control communication systems, or C2CS, prior to entering a battle space and provides the ability to forward this information off to advance commanders. Not only does this increase the awareness of the air crew, but also acts as a force multiplier in expanding the reach of C2CS.

With 70 years of history as one of the most versatile and battle-tested aircraft in the Air Force fleet, the C-130 looks to enter its next era in the reoptimization for Great Power Competition – and just as Robins AFB has kept the aircraft flying the last seven decades, it will be sending out the aircraft to maintain air dominance for years to come.

By Patrick Sullivan, 78th Air Base Wing Public Affairs