On August 17, the USS Nautilus and USS Argonaut were off the coast of Makin Atoll in the pacific. They were carrying 221 Marine Raiders. The Raider’s objectives were to destroy the Japanese garrison and installations, take prisons so they could be interrogated, and finally, the Gilbert Islands must be reconnoitered. It was also meant to divert Japanese attention and reinforcements from the Allied amphibious invasions on Guadalcanal and Tulagi.

Even with two 100-meter super-subs, A and B Company could only fit 221 men, so they left without a platoon from each. Maj. James Roosevelt, the president’s 35-year-old son, was one of Carlson’s targets. After serving as FDR’s political consultant and covert diplomat, the young Roosevelt joined the Marines. As a Raider enthusiast, he convinced his father to let him join.
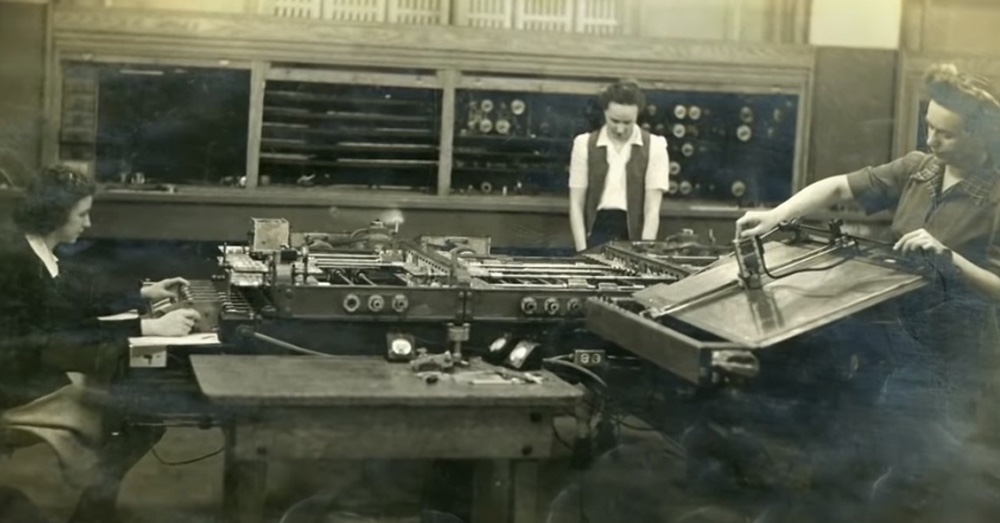
Raiders were stuffed inside vacant torpedo tubes during travel. Submarine ventilation techniques couldn’t prevent thin air and high temperatures. The boats would surface for ten minutes twice a day to let the Raiders exercise and breathe fresh air before ducking back into the Pacific to avoid air assault.
The two submarines surfaced outside Makin’s coral reef at midnight on August 16–17 to find turbulent conditions. The first two LCRL rubber boats sank in the surf. The remaining launches’ uninsulated 6-horsepower engines were flooded with seawater and failed to ignite. Carlson felt his two-pronged approach would be too difficult to accomplish in the inclement weather and ordered A and B company to land together. In the chaos, the boat carrying Lt. Oscar Peatross and 11 Raiders missed the orders and headed west.
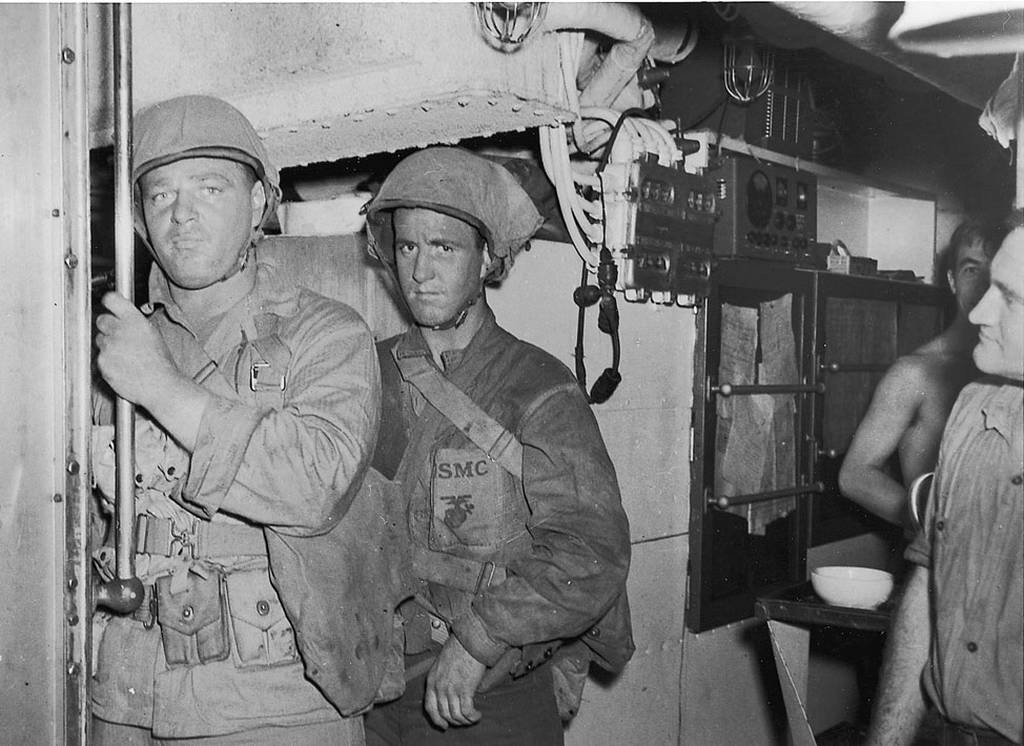

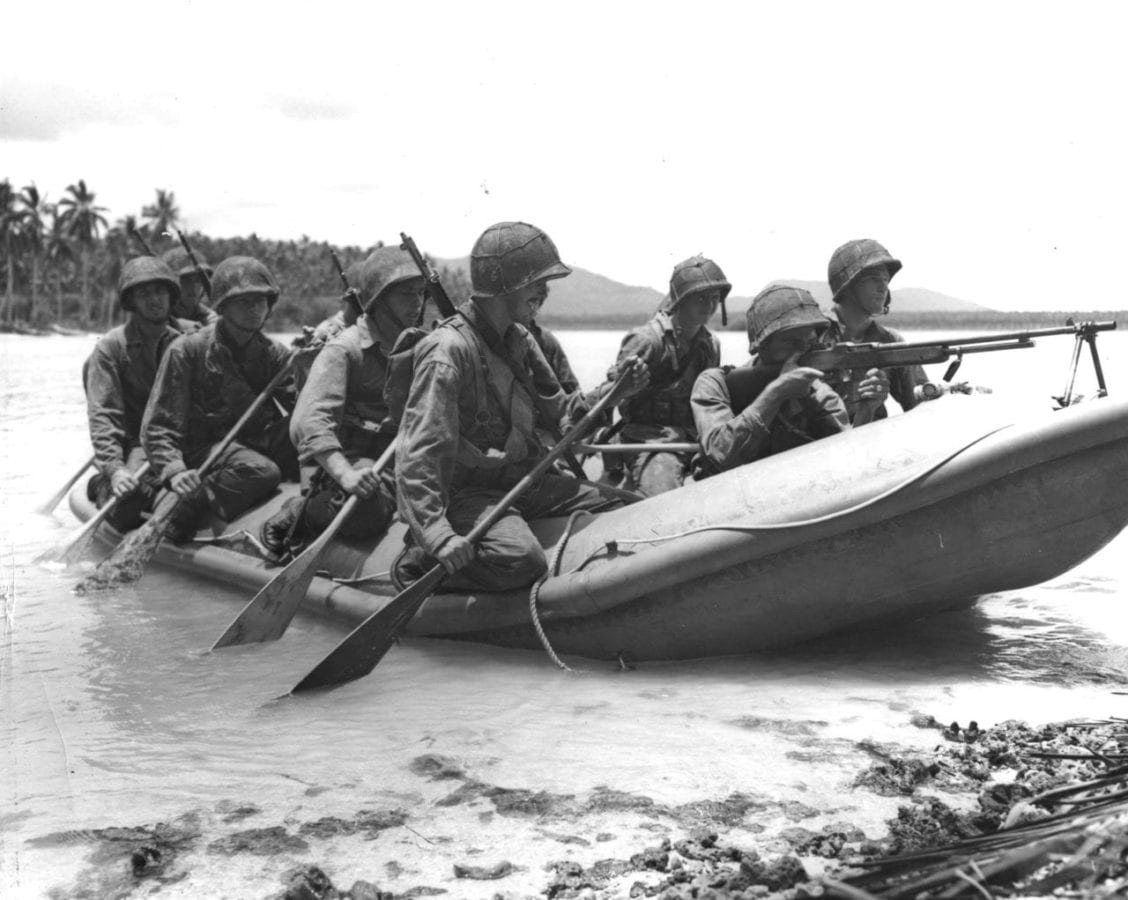
Carlson’s Raiders landed about 5 AM after battling the waves for an hour, with some troops scattered but undetected. Carlson’s invention was to divide his squad into three fireteams, each with one rifleman with a semi-automatic M1 Garand for distance shooting, another with a Thompson submachinegun for close-range firepower, and a Browning Automatic Rifle gunner to give covering fire. Heavy armaments included.30 caliber light machine guns and.55 caliber Boys anti-tank rifles were requisitioned from the Canadian Army by Carlson.
On landing, a Raider unintentionally fired his BAR, ruining any chance for surprise. The garrison’s commander, Chief Petty Officer Kyuzaburou Kanemitsu, had been alert days earlier. His men deployed by bike and truck to fight the American invaders. Misadventures continued when the Raiders kidnapped a Japanese soldier but shot him when he escaped.
Carlson met Makin locals who spoke pidgin English. They were pleased to help the Americans and said 160 to 300 Japanese were on the island, and they were ready. The Raiders maintained their march until 6 AM when Lt. Le Francois’ scouts sighted Japanese forces dismounting from vehicles.

Le Francois ambushed his platoon in a breadfruit grove on high ground. Sgt. Clyde Thomason adjusted the men’s positions as Japanese skirmishers neared. When the Japanese got close, the marines opened fire, killing the closest attackers and exploding the truck’s engine with an anti-tank rifle.
The Japanese answer was fatal. Four Type 92 Lewis machine guns raked Raider positions, killing Sgt. Thomason and injuring Le Francois. Posthumously, Thomason became the first enlisted Marine to win the Medal of Honor. Camouflaged shooters killed Lt. Jerry Holtom and four radio operators among palm palms.
Carlson quickly added the 2nd Platoon, which lost nine men in 15 minutes, and B Company. Raider machine gunner Cpl. Leon Chapman fired 400 rounds into a Japanese machine gun nest at 200 meters. After inspecting the silenced weapon, Chapman “nearly threw up” when he discovered he had slain a dozen Japanese who had sacrificed themselves to man it.
Twelve of Peatross’ forces landed at the second landing zone and proceeded uncontested into the barracks and the defender’s command position. An isolated squad shot six astonished Japanese before being held down by an LMG crew. Pvt. Vernon Castle was struck multiple times as he advanced, but he threw a grenade and killed three before dying.
After that, Peatross’ marines fired a car speeding towards the command post, blew up a radio and a truck full of ammo, and retreated to the Nautilus, losing two more troops. In the chaos, they killed Kanimetsu, who destroyed confidential documents and conveyed the message, “We are dying defending the island.”

The Nautilus began bombarding Japanese positions with two dozen shells when Carlson learned from natives that hostile ships were in the lagoon. Unwilling to risk a shore battery’s fire, the Nautilus arced 65 6-inch shells into the lagoon. By luck, indirect fire sank two ships, igniting a transport and a patrol boat and mistaking a hostile plane for a bird, the submarine dove, ending naval gunfire support. The Japanese assaulted the Raiders, attempting to swarm them failed, and the assailants were all killed at close range. Undeterred, the bugle played again, and the Japanese launched a second suicide strike, wiping out Kanimetsu’s marine platoon. A few dozen survivors continued to shoot intermittently. Fearing more reinforcements, Carlson chose not to strike the Japanese position. At 1:30, air support arrived. Twelve Mitsubishi F1M floatplanes bombed and strafed the island for an hour, driving the Raiders fleeing but not inflicting any fatalities. Then an F1M and a Kawanishi flying boat landed in the lagoon. The Raiders fired machine guns and anti-tank rifles at the aircraft, setting it on fire. The seaplane with scores of men managed to land. The intensity of incoming fire must have given the pilot second thoughts as he taxied on the water and took off again before landing.
The colonel decided to withdraw to submarines at 7 PM as planned. When they returned to the ocean, his troops discovered their boats’ motors had stopped working, and the waves and weather made it difficult to paddle back to the submarines. Exhausted Raiders dropped their ineffective launch motors and spent five hours trying to force through severe waves, losing most of their weapons and supplies. Eleven of 18 boats reached the American subs. By nightfall, Carlson, Roosevelt, and 70 injured Raiders remained on Butaritari. Individual boats continued to battle the waves the following day, including one with Roosevelt onboard. A five-person crew led by Sergeant Allard volunteered to row back to the atoll with a rope the Raiders could use to board the submarine. A squadron of Japanese jets bombed the Nautilus halfway through its launch. The subs crash-dove, and the jets strafed the rescue squad, killing them. After reassessing the situation, Carlson opted to finish the mission on Makin. The Raiders scavenged Japanese weapons to replace those washed away and sabotaged a derelict seaplane facility while avoiding air assaults. They burned much of the facility and 1,000 aviation fuel drums. Carlson decided his forces had a greater chance of reaching the submarines from the lagoon because it had no shore armament.

He encouraged the Nautilus’s captain to enter the lagoon using a semaphore lamp and a dinner chat they had earlier. The Raiders paddled on a raft of three launches, two working outboard engines, and local canoes as outriggers. The Indians gave them a canoe and buried their dead in exchange for USMC combat knives. The new boat reached the submarines, and the Raiders set sail for home. Among the 17 wounded soldiers, four surgeries were performed on the submarine’s mess table. The injured soldiers all survived.
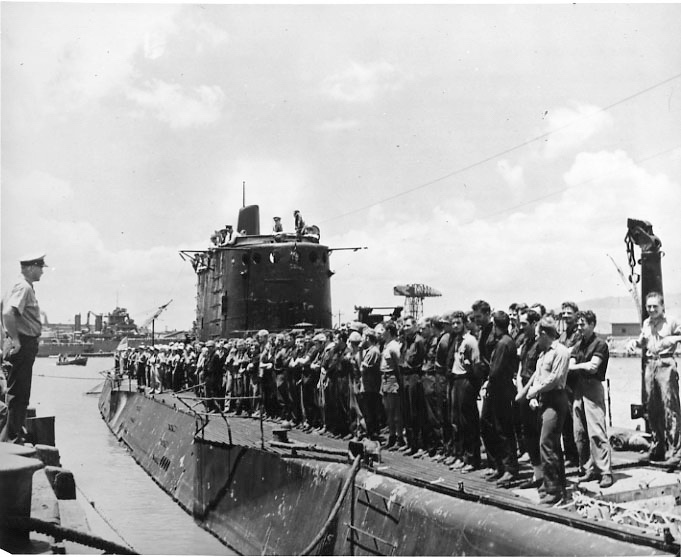
On August 27, Carlson’s Raiders returned to Pearl Harbor to a hero’s welcome. They reported 18 dead and 12 MIAs and killed 160 enemies. According to Japanese records, 46 base personnel and an undisclosed number on Japanese boats and planes died.