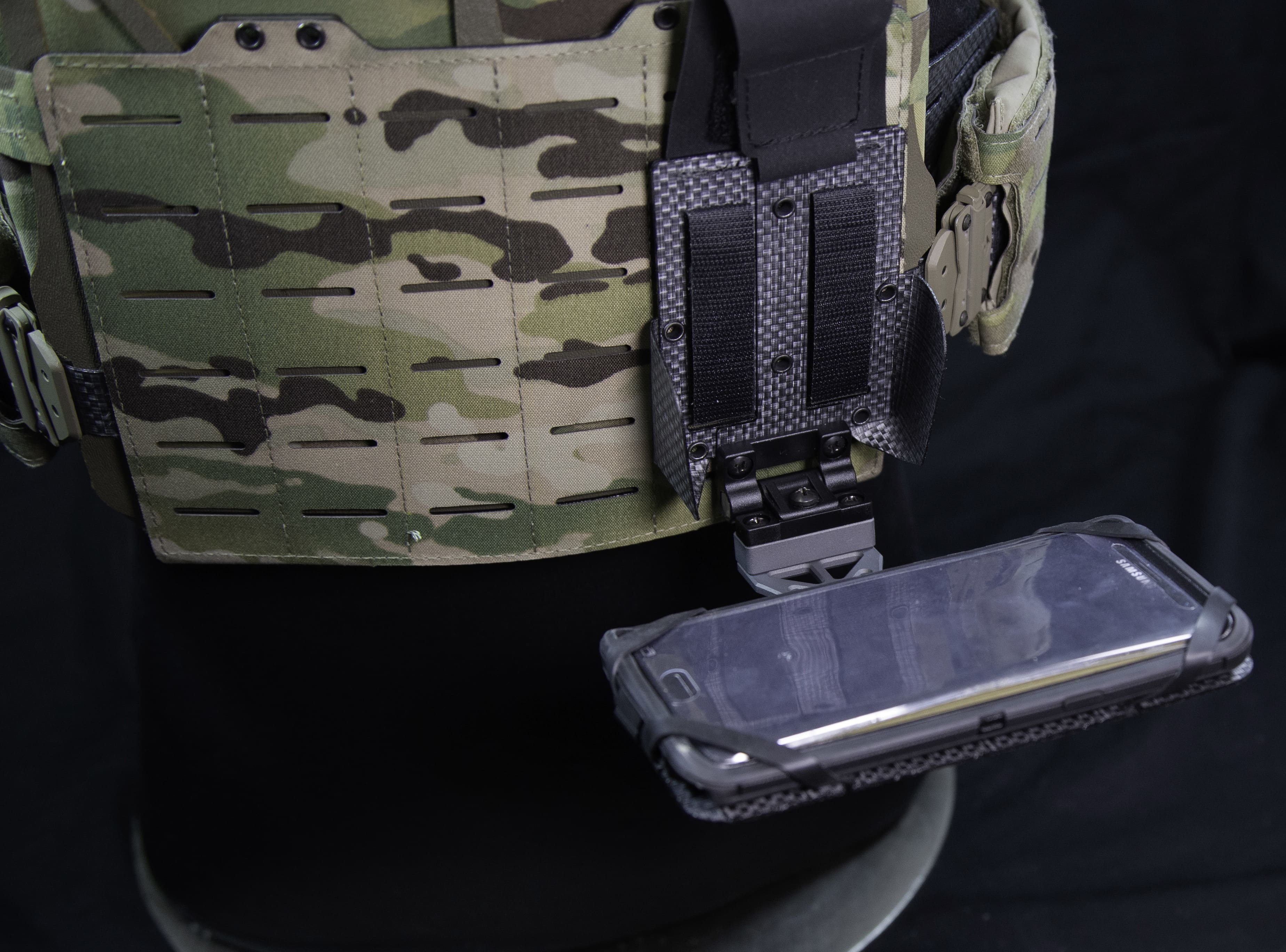
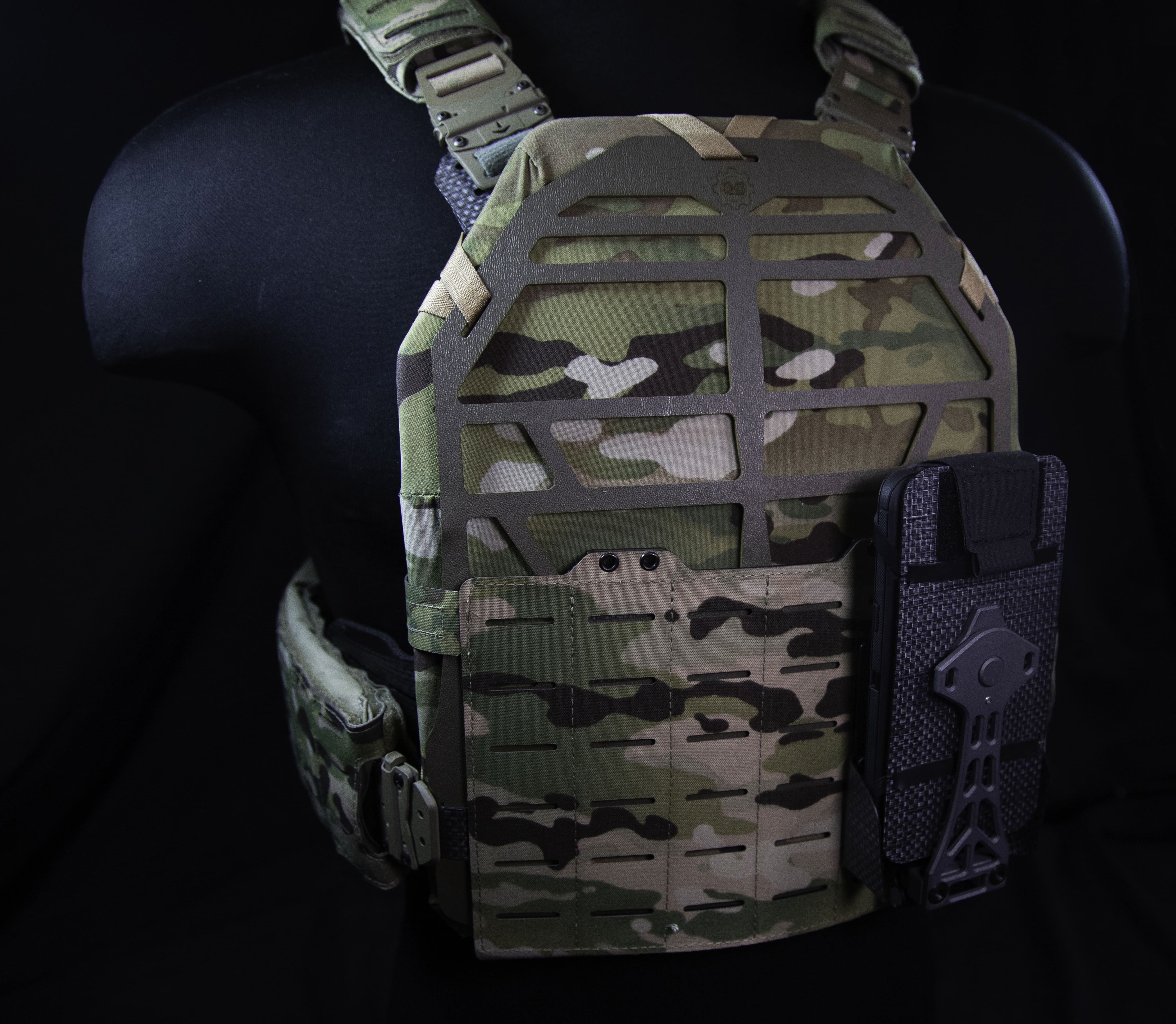
FORT BRAGG, N.C. — Operational testing of the Army’s newest precision rifle, the Compact Semi-Automatic Sniper System (CSASS) began recently, marking one of the final hurdles this system will face prior to fielding.
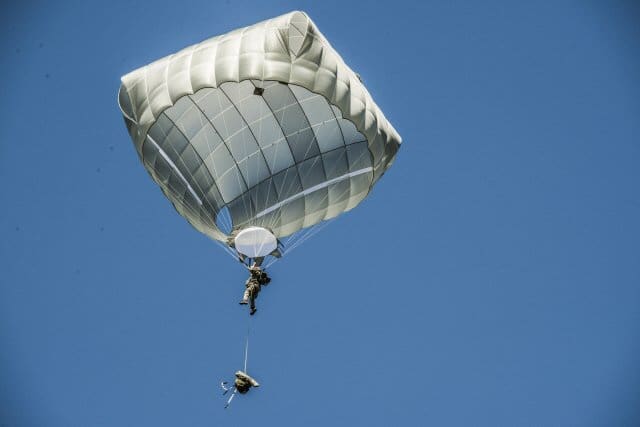

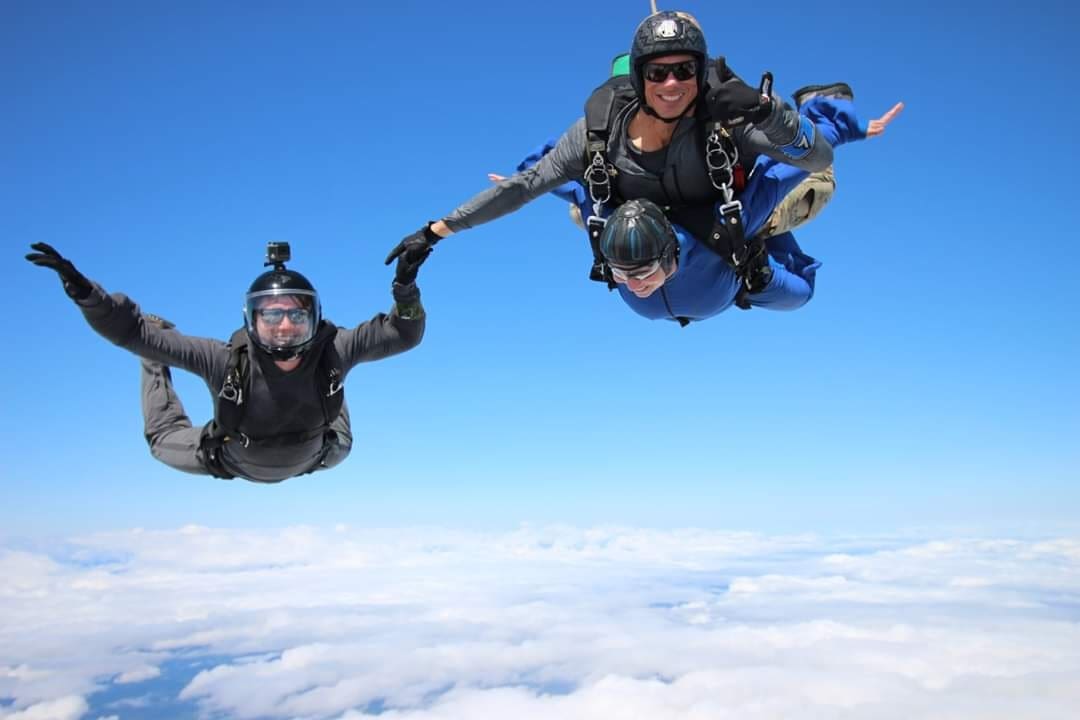
Snipers assigned to the 82nd Airborne Division recently participated in airborne infiltration test trials of what could potentially be the Army’s newest sniper system.
“The compact nature of the CSASS is appealing to airborne forces and particularly Snipers who are typically armed with long barreled precision rifles,” said Sgt. 1st Class Ross Martin, a Test NCO with the U.S. Army Operational Test Command’s Airborne and Special Operations Test Directorate (ABNSOTD).
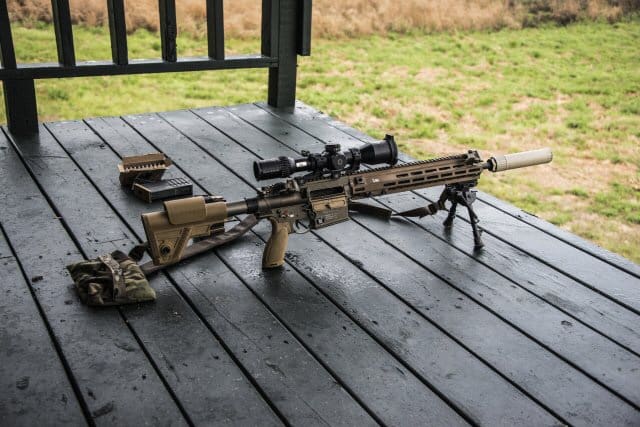
“Current sniper systems are equipped with 20-inch barrels, sound suppression systems and full length stocks that provide accuracy and a stable firing platform required of any precision rifle,” said David Parris, a CSASS New Equipment Training (NET) trainer from the U.S. Army Tank-automotive and Armaments Command’s Soldier Weapons Support.
Being a product of battlefield evolution, the CSASS is more geared toward operations in urban environments and operating in and around armored vehicles where traditional length sniper systems can be cumbersome.
“The CSASS will feature a reduction in overall length (with the suppression system attached) and an adjustable stock that provides maneuverability and promotes a stable firing position,” said Victor Yarosh of Project Manager Soldier Weapons.
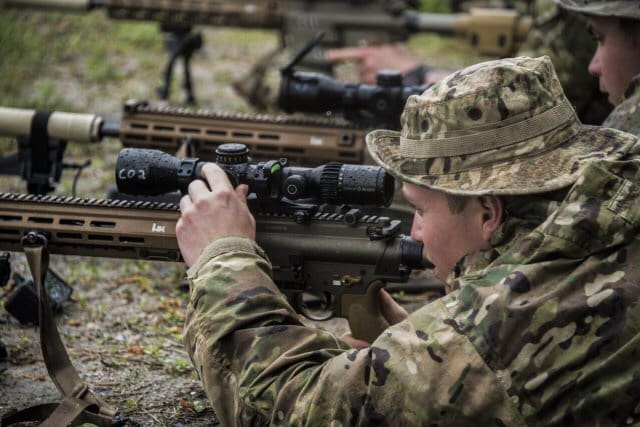

This will provide airborne snipers a more compact load during airborne infiltration operations and provide a precision rifle platform more conducive to their combat environment without reducing their lethality.
Spec. Nicholas Farmer of Orlando, Florida, a Sniper in C Troop, 1st Battalion, 73rd Cavalry Regiment immediately identified the attributes of a more compact precision rifle.
“The CSASS is much shorter and lighter than our current system which will make long dismounted movements and reaction to contact more efficient,” he said.
Spc. William Holland from Sylacauga, Alabama, a sniper with 2nd Battalion 508th Parachute Infantry Regiment echoed his fellow snipers assessment as, “lightweight and compact makes for a more manageable load during post drop operations.”
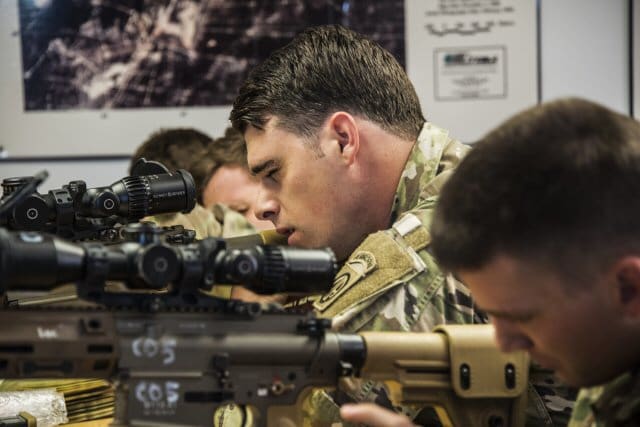
Prior to testing, Snipers participated in a NET which included familiarization with the system, maintenance, target engagement and zeroing procedures.

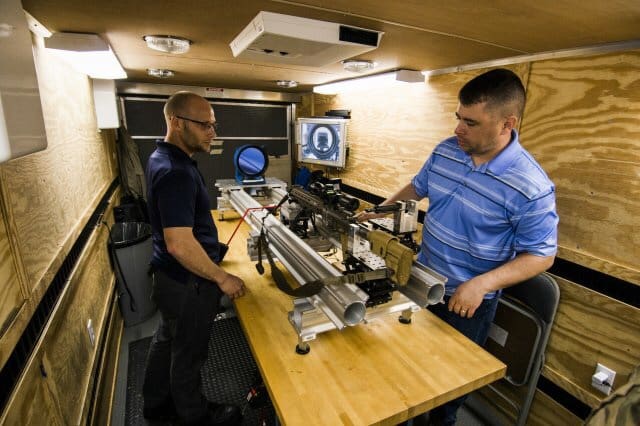
The critical task in testing any small arms platform intended for use by airborne forces is ensuring zero retention of the primary optic subsequent to airborne insertion. This is a critical gauge of the paratrooper’s lethality during airfield seizure and other follow on operations.
“This process establishes a baseline for site reticle locations prior to and post airborne insertion,” said Lacretia Cook, an instrumentation technician with the ABNSOTD.
“Testers can monitor any ‘shift’ in the weapons sight reticle.”
To evaluate this performance measure of the CSASS, the ABNSOTD test team employed the organization’s mobile weapons boresight collimator to ensure the snipers’ “pre-mission” zero was not degraded by shock associated with parachute infiltration.
Once this data was collected, snipers conducted a known distance live fire exercise to gauge lethality subsequent to static line and military free fall operations.

For Sgt. Christopher Landrum of Delano, California, the target audience of trained snipers was perfect.
“It’s vital that operational troops are the ones testing the system as they are best suited to recognize system requirements and mission capabilities,” he explained.
Sgt. 1st Class Darin Pott, a senior sniper with the 1st Battalion, 73rd Armored Regiment said he would also like to see Soldiers added to the process earlier.
“The Army should involve the sniper community at the earliest possible milestone of development,” he said.
“Operational Testing is about Soldiers. It is about making sure that the systems developed are effective in a Soldier’s hands and suitable for the environments in which Soldiers train and fight,” said Col. Brad Mock, Director of ABNSOTD.

“OTC is the U.S. Army’s only independent operational test organization,” said Lt. Col. David Dykema, deputy of ABNSOTD’s Test Division.
“We test Army, Joint, and Multi-service airborne and airdrop related warfighting systems in realistic operational environments, using Soldiers to determine whether the systems are effective, suitable, and survivable.
“Any time Soldiers and their leaders get involved in operational testing,” he added, “they have the opportunity to use, work with, and offer up their own suggestions on pieces of equipment that can impact development of systems that future Soldiers will use in combat.”
Story by Mike Shelton, Airborne and Special Operations Test Directorate, U.S. Army Operational Test Command Public Affairs
Photos by Mr. Chris OLeary, Videographer, Airborne and Special Operations Test Directorate, U.S. Army Operational Test Command Public Affairs