Even before we were a nation, we had an army…
Even before we were a nation, we had an army…
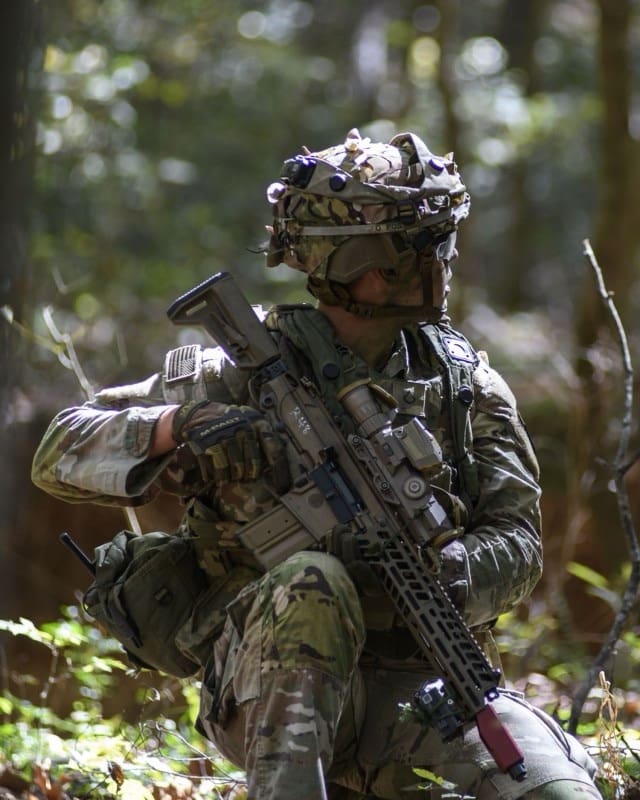

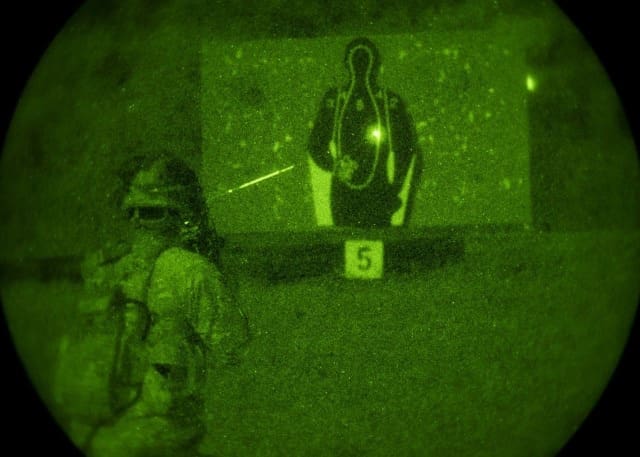
FORT JOHNSON, La. — Amidst the evolving landscape of military acquisitions and the Army’s renewed commitment to agile, rapid capability development, the Next Generation Squad Weapon (NSGW) has undergone a pivotal Expeditionary Operational Assessment (EOA) in collaboration with elements of 1st Brigade, 101st Airborne Division (Air Assault), at the Joint Readiness Training Center (Rotation 25-07).
This assessment marks a significant step forward in the Army’s implementation of the continuous transformation framework, specifically within the Transformation in Contact (TiC) phase.

The 101st Airborne Division, identified by the Army as one of its TiC units, plays a critical role in rapidly integrating and evaluating emerging capabilities that directly address urgent operational requirements.
Operational Testing in TiC: A New Paradigm
The NGSW assessment at Fort Johnson is in direct response to Army Chief of Staff Gen. Randy George’s call to action for the Army to swiftly adapt its acquisition processes. Through the continuous transformation framework, TiC-designated units receive and rapidly implement new capabilities at a relevant speed. This has necessitated a shift in thinking from traditional test and evaluation (T&E) approaches, in trade for more agile, iterative processes. These highlight the integration of rigorous data-driven analysis and direct soldier feedback.
“Our commitment to providing world-class, objective test data to Army senior leaders remains unchanged. But the rapidly changing battlefield requires that we rethink historical methods and processes of operational testing. TiC especially highlights that we cannot remain in the status quo,” said Col. Mike Trotter, Director of the Maneuver Test Directorate (MTD), U.S. Army Operational Test Command (USAOTC). “We are embracing agility and broadening our testing horizons, while ensuring we retain world-class standards.”
Small Team, Big Impact
Whereas operational testing has traditionally been a large-scale effort — requiring extensive planning, coordination, and strict control of test variables — T&E within TiC has sparked more agile practices. EOAs are one such evolution.
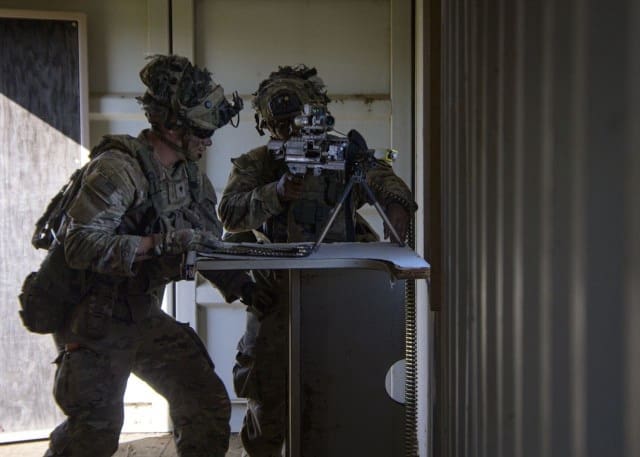

This EOA event, which expands upon previous assessments conducted at Fort Campbell, Kentucky, is led by a specialized, nimble test team uniquely equipped for agile testing. The team is drawn from USAOTC’s MTD, Dismounted Test Division — Mr. Troy Willey, a retired Command Sergeant Major with extensive armored command experience; Mr. Bill Rabena, a mathematician, operations research systems analyst and former brigade commander with deep expertise in operational analytics; and Maj. Thomas Lorenson, the senior test officer. They are joined by Maj. Matt Brooks, a military evaluator from the U.S. Army Evaluation Center.
“The expertise of Mr. Willey and Mr. Rabena, as well as Maj. Brook’s operational experience, [are] invaluable,” emphasized Lorenson. “Their operational and analytical insights significantly enhance our ability to construe soldier feedback comprehensively and accurately. I’m fortunate to work alongside such a proficient and dedicated team of experts.”
Expanding the Testing Frontier
The broader shift toward EOAs was successfully applied in previous programs, such as the Infantry Squad Vehicle and Next Generation Tactical Vehicle. EOAs prioritize flexibility, mobility, and timely data collection within operationally realistic training and combat scenarios.
This EOA also reflects growing engagements between operational testers and the Combat Training Centers (CTCs). CTCs are uniquely poised to enable testers minimal, invasive access to TiC units in their training cycles. CTC conditions, in many cases, qualify as the operational realism required of traditional operational tests.
Col. Ricky Taylor, Commander of Operations Group at Joint Readiness Training Center, underscored this critical initiative. “We need to continue adapting to changes on the battlefield and replicate large-scale ground combat operations,” he said. “These assessments directly support the chief’s and the Army’s initiatives. It’s imperative we embrace them and fully integrate these assessors with our task force to achieve the most valuable operational data.”

Another key evolution was the integration with the Centers of Excellence (COE), as a source of evaluation criteria. This nascent approach seeks to align EOA data requirements with the learning demands of the COEs and, in some cases, the operational units. This marks a shift from traditional dependence on formal requirements documents, like the Capability Development Document, which may be outdated or absent in today’s rapidly evolving environment.
“The Army’s expectations are clear: operational testing must deliver timely, relevant insights without compromising rigorous evaluation,” explained Willey. “Our approach ensures rapid adaptation to soldier and unit needs, directly informing future capability development.”
Qualitative Insights, Quantitative Precision
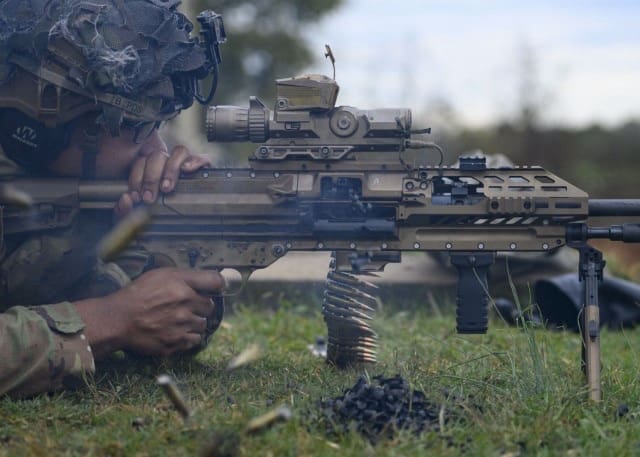
During the assessment, the team conducts comprehensive qualitative and quantitative surveys with Soldiers, which captures broad perspectives on the NGSW’s 6.8mm ammunition, Fire Control System, and overall weapon implementation. Hundreds of Soldiers provide immediate, unfiltered insights highlighting both strengths and areas requiring improvement.
“The weapon is great. I can fire effectively from all positions, and it gives me a lot of confidence,” said Spc. Shaquille Pusey of Alpha Co., 1-506th Battalion. “My only issues are the bipod, which can be hard to manage, and the ammo pouch release button. It often comes undone when I move, spilling the link.”
“With this weapon, I’m simply more lethal,” said Sgt. Christopher Caldwell from 3rd Platoon, Alpha Co., 1-506th Battalion. “Engaging targets at long distances feels effortless. It’s like having a cheat code. The precision and controllability give us a clear edge.”
While qualitative soldier feedback provides firsthand experience, Rabena’s system-oriented approach ensures the rigorous analytical depth required in operational testing.
“Unique to this EOA is its targeted data collection approach, which focuses on specific areas needing improvement that were identified in a previous operational test’s database,” Rabena said. “This EOA serves as a litmus test for program manager (PM) progress and unit sentiment toward the new system. It essentially asks, what still needs to be fixed, and have any new issues emerged?” This structured data collection will yield precise, actionable feedback for evaluators like Brooks, who ensure system updates, while contributing to the iterative process.
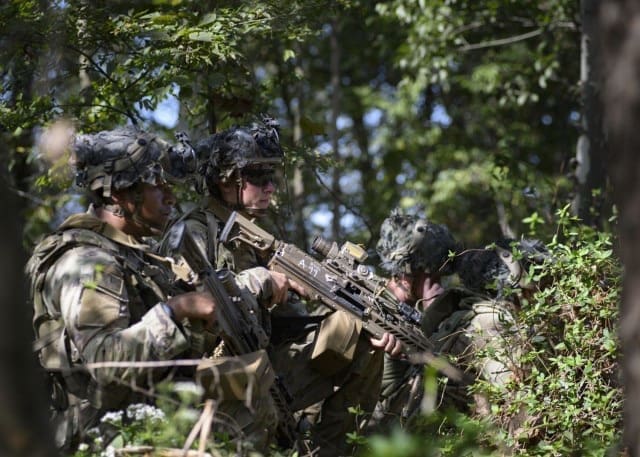

“The Next Generation Squad Weapon program thrives on rapid prototyping and embedded evaluation,” said Brooks. “Soldier feedback drives iterative improvements at the speed of relevance, ensuring design adjustments meet real-world needs. The U.S. Army Evaluation Center accelerates the process by delivering results briefs to senior leaders within seven days of test completion.”
Unbiased Testing, Unchanged Integrity
While TiC assessments accelerate fielding timelines and challenge traditional test methodologies, USAOTC’s fundamental commitment to providing unbiased data for decision makers remains unchanged. Modernizing T&E capabilities and data collection methods, as well as fostering closer integration with new stakeholders across the acquisition and operational communities, enables the generation of critical insights under realistic operational conditions, free from personal bias.
“Our role as an impartial stakeholder is absolutely critical,” Lorenson noted. “We objectively report the data, bridging soldier experiences with the needs of program managers and the larger enterprise, ensuring rapid delivery of reliable and effective equipment.”
A Call to Action, A Call to Transform
The assessment at Fort Johnson directly aligns with the recent emphasis of Maj. Gen. John Klein, Special Assistant to the Commanding General, U.S. Army Training and Doctrine Command on incorporating lessons learned from global conflicts that highlight urgent operational realities. The continuous transformation framework, as demonstrated through TiC, ensures that soldier input, rigorous operational testing, and adaptive acquisition practices remain at the forefront of Army capability development.
“The Chief of Staff and Klein’s message to the force reemphasized the need to evolve iteratively and continuously,” said Rabena. “This assessment isn’t just about one weapon system. It represents the future of how we rapidly develop and field critical capabilities to Soldiers on the ground.”
Forward Momentum: Lessons and Insights
As the assessment concludes, USAOTC will produce a memorandum of observation highlighting critical improvements, agile spin-off opportunities, and valuable insights to guide ongoing and future acquisition efforts. By providing data-backed, field-tested insights, iterative feedback empowers both the developers and decision makers to innovate and deliver with the urgency of today’s battlefields demand.
“Our ultimate aim is timely feedback that enables PMs, Soldiers, and the broader acquisition community to swiftly and effectively deliver superior capabilities. The NGSW Expeditionary Operational Assessment at Fort Johnson exemplifies our commitment to transforming operational testing to meet the urgent demands of the modern battlefield,” concluded Lorenson.
“We are zealously looking at how we can assist meeting the demands of operational realities, continuous transformation, and the forthcoming sweeping changes across the Army Acquisition enterprise,” Trotter said. “What we do for our Army aids in providing the best equipment on the planet to our Soldiers so that they can fight, dominate, win, and survive on the battlefields in which they WILL find themselves. The NGSW EOA is a significant step forward in revolutionizing operational test and evaluation.”
By CPT Simeon Blakely, MAJ Thomas Lorenson, and Mr. Thomas Mort, Maneuver Test Directorate, U.S. Army Operational Test Command

Washington (June 11, 2025) – In response to current world events and in support of the strategic objectives outlined in the Army Transformation Initiative, the U.S. Army has issued a termination for convenience of the current low-rate initial production of the M10 Booker Combat Vehicle and will not enter into full-rate production as originally planned.
The Army will request to reallocate the remaining funds in fiscal 2025 to accelerate fielding of war-winning capabilities and anticipates additional significant savings to be fully realized within the next 18-24 months.
Formerly known as the Mobile Protected Firepower, the M10 Booker low-rate initial production contract was awarded in June 2022 to General Dynamics Land Systems for the production and fielding of up to 96 vehicles. The ongoing contract termination process will ultimately determine the disposition of the remaining assets.
Although M10 Booker production will conclude, the Army appreciates the efforts of the team and Soldiers from the 82nd Airborne Division who worked on the program.
By U.S. Army Public Affairs

FOREST PARK, Ga. — The Georgia Army National Guard made history with the activation of the 111th Electromagnetic Warfare Company, the first unit of its kind in the U.S. Army.
The ceremony, held at the Fort Gillem Enclave, also included the assumption of command by Capt. Caleb Rogers.
Lt. Col. Luke Gurley, commander of the 221st Intelligence and Electronic Warfare Battalion, the parent command of the 111th EW, presided over the ceremony.
“Today we activate the 111th Electronic Warfare Company, a unit that will be at the forefront of our capabilities in the electromagnetic spectrum,” Gurley said.
The activation of the 111th EW Company marks a significant step in modernizing the Army’s capabilities within a domain that is increasingly critical to national security. This new formation will provide capabilities to detect, recognize, locate and identify signals of interest, supporting combatant commanders.
During his remarks, Gurley said the activation aligns with the philosophy of U.S. Army Chief of Staff Gen. Randy George, who advocates for rapidly modernizing units and equipment based on emerging needs and technology. He also believes every unit will need to master the electronic warfare fight.
“The legacy of the 221st Intelligence and Electronic Warfare Battalion and the Georgia Guard to lead from the front and provide those critical capabilities to support the warfight both locally and abroad is going to be driven by Georgia Soldiers,” said Brig. Gen. Theodore Scott III, commander of the 78th Troop Command. “And that means the world to me.”
Scott, once the leader of the 221st IEW, has watched the formation grow over the years.
“As the battlefield continues to evolve, the 221st IEW is ready,” Scott said. “It’s one of the most deployed units in the state and has been for a number of decades. And so that continues to articulate the relevancy of 221st and now the 111th.”
The 221st IEW has deployed Soldiers to Afghanistan, Iraq, Kuwait, Syria, Jordan, Turkey, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, Kosovo, Cuba and the southern border, and has supported U.S. Central Command and U.S. Indo-Pacific Command activities.
The 111th EW Company traces its lineage to the 1st Battalion, 111th Signal Battalion, the only Georgia Army National Guard unit mobilized during the Berlin Crisis in 1961 and the first unit mobilized since the Korean War.
“Today is not simply about activating a new unit. It’s about recognizing and honoring a proud legacy,” Gurley said.
Rogers, the newly appointed commander, acknowledged the unique challenges and opportunities associated with leading this pioneering unit. He said he is charged with coordinating with relevant schools and units to train on developing systems as the Army continues to identify and finalize the necessary training for the unit’s capabilities.
“No Soldier in the 111th ended up here through recruiting,” Rogers said. “They knew what they wanted when they came to the 111th. They knew that they wanted to rebuild Army EW.”
Rogers said the company will provide division commanders with four platoons of electromagnetic warfare teams, with a total of more than 80 Soldiers.
“All of our Soldiers are expected to keep up with evolving technology, and the unit as a whole is remaining flexible with the expectation of receiving a growing number of mission types,” Rogers said.
He also confirmed that the 111th EW Company will conduct its first field exercise in August at the Chattahoochee National Forest, focusing on electromagnetic support training and identifying and locating static and moving targets, including helicopters provided by the Georgia Guard’s 78th Aviation Troop Command.
“It’s a great time to be in military intelligence and electromagnetic warfare,” Scott said. “I am excited for the future.”
By Charles Emmons, Georgia National Guard
The Army is rapidly advancing capabilities in the Short-Range Reconnaissance (SRR) program by deploying cutting-edge Small Uncrewed Aircraft Systems (SUAS) to Transformation in Contact (TiC) Brigades.

These modernized systems amplify combat power and lethality, improve troop survivability, and give commanders real-time intelligence on the modern battlefield.
COL Danielle Medaglia, UAS Project Manager, highlighted the importance of the Army’s approach.
“The technology across the UAS environment is evolving at a rapid pace,” Medaglia said. “Therefore, in parallel to fielding the next tranche of SRR we are already working on future capabilities, leveraging new mature technology and quickly iterating on Soldier feedback.”
“Continuous iteration and integration of new technology, multi-vendor awards, and continuous competition ensures we can field the most capable and cost effective UAS, at scale, that aligns with Soldier needs.”

SRR systems are integral to modern warfare. Equipped with advanced sensors, these SUAS provide real-time intelligence, reconnaissance, and target acquisition, empowering commanders with swift decision-making capabilities. Acting as force multipliers, they enable precise fires, support ground operations with timely information, enhance operational flexibility, and crucially, improve troop survivability by detecting threats and identifying safe routes.
Equipping of Next-Generation SUAS Capabilities
The Army continues to use a multi-vendor approach to drive competition and deliver technology at the speed of relevance.
“The rapid deployment of Tranche 2 SUAS to our combat teams is a testament to our commitment to providing Soldiers with the most advanced tools available,” said BG David Phillips, Program Executive Officer, Aviation. “These systems are not just about technology; they are about enhancing our operational capabilities and ensuring the safety and effectiveness of our troops on the ground.”
In April, PEO Aviation’s UAS Project Office responded to an urgent request to deploy Tranche 2 SUAS to the 1st Brigade Combat Team of the 101st Airborne Division (Fort Campbell, Kentucky) in support of their rotation at the Joint Readiness Training Center (JRTC) at Fort Johnson, Louisiana.
Demonstrating the Army’s ability to rapidly equip its forces, Skydio X10D systems were delivered to the 1/101st, under the Army’s TiC 2.0 initiative within one month of the request. Additionally, Teal Drones’ Black Widow system is preparing to field. Both Skydio and Teal will support Army TiC Brigades in developing and refining tactics, techniques, and procedures for employing networked reconnaissance and surveillance systems against emerging battlefield threats.
The Army’s Vision for the Future of SRR
The deployment and evaluation of these SUAS are part of a larger Army initiative focused on “Transforming in Contact” – evaluating uncrewed aircraft systems and aligning personnel and tactics with new technologies. The Tranche 2 system is built upon Soldier feedback with improvements such as enhanced autonomy, a new ground control station, and modular architecture.
The Army remains steadfast in its mission to strengthen Soldier lethality, creating a force that can dominate in large-scale combat operations across multiple domains.
“The modern battlefield is changing. I think we’ve seen that,” said Gen. Randy George, Chief of Staff of the Army, during a recent interview. “We’ve learned a lot over the last year and a half with our transformation in contact. So, this is bottom-up innovation that we know we need, and we know we’ve been watching what’s happening on the modern battlefield.”
From Program Executive Office, Aviation
AUSTIN, TX—June 10, 2025— Ultra I&C has been selected by the U.S. Army to provide its troposcatter system. This initial award will get Archer into the hands of U.S. Army soldiers for training and evaluation to enhance network resiliency by adding an additional form of secure communications.

Archer™ Troposcatter technology represents a critical communications capability in contested environments where satellite access may be denied or degraded. Archer delivers high- throughput beyond-line-of-sight communications exceeding U.S. Army range requirements by maintaining secure links without relying on satellites or ground-based infrastructure. Enhanced with advanced encryption and anti-jamming features, Archer deploys in under 20 minutes and meets all required Military Standards (MIL-STD) for operations in the most challenging environments. Through rapid innovation cycles, Ultra I&C developed Archer to outperform legacy systems while significantly reducing size, weight, power and cost.
“The Army requires resilient communications solutions to meet mission requirements while operating in the most demanding operational environments,” said Jeffrey Wrobel, vice president of business development for Ultra I&C’s Communications division. “In the landscape of congested modern warfare and the real possibility of a day without satellites, troposcatter is an essential technology.”
Archer is built on a modular, upgradeable platform and is interoperable with existing U.S. Army systems, ensuring seamless integration.
Ultra I&C delivers defense technology solutions including a comprehensive suite of high- capacity tactical communications systems spanning line-of-sight, troposcatter, and satellite technologies—providing resilient, multi-layered communications networks for modern warfighters across all operational domains.

FORT EISENHOWER, GA.—The U.S. Army has officially designated the 17A Analytic Support Officer (ASO) role as a Key Developmental position for Captains (Capt.) and Majors (Maj.), a pivotal step aimed at bolstering the Cyber Mission Force’s ability to detect, analyze and counter sophisticated cyber threats. This designation, effective Fiscal Year 2025, underscores the Army’s recognition of the increasing importance of data analytics in modern warfighting.
The career path adjustments outlined in the Department of the Army Pamphlet (DA PAM) are primarily shaped by senior leaders within the Cyber and Electromagnetic Warfare (EW) communities. These leaders have long emphasized the criticality of ASOs, whose expertise in identifying adversaries within networks absent prior signatures forms a cornerstone of defensive cyber operations.
“Analytic support officers are force multipliers,” said the chief of cyber, Col. John Hosey. “They build the analytic scheme of maneuver that allows us to observe and understand adversaries in contested environments. The Army’s shift toward recognizing data as essential to warfighting functions reflects what we in cyber have understood for almost a decade0, given the nature of the domain.”
A Strategic Move for Talent Retention and Promotion
Elevating the ASO role to a Key Developmental position directly impacts talent management and career progression within the cyber force. Historically, technical expertise has not always translated into promotional advantage within traditional Army structures. With this change, officers specializing in advanced analytics now have a more straightforward pathway for career growth, acknowledging their contributions to mission success.
By formally incorporating the ASO role into the Key Developmental framework, the Army enhances the visibility and prestige of these officers, aligning their career trajectory with leadership expectations. This move also signals to the broader force that analytical prowess and cyber expertise improve mission and lethality and are indispensable components of national defense.
The Analytical Edge in Cyber Warfare
Analytical Support Officers dissect enormous datasets—including network traffic, endpoint logs, and diverse digital intelligence—to uncover adversary tactics. Their advanced methodologies range from statistical modeling to machine learning-driven detection techniques that identify evolving threats.
These officers leverage mathematics, programming, and deep domain expertise to grant commanders essential situational awareness, enabling rapid, informed decision-making. As cyber warfare intensifies globally, ASOs remain at the forefront, pioneering automation techniques to proactively identify and mitigate emerging cyber threats.
“The Army strategically places its most capable individuals in roles with the greatest impact, presenting the most complex challenges,” said the Principal Analytics Officer, U.S. Army Cyber Command, LTC Jacob Youmans. “The ASO exemplifies this, requiring expertise in mathematics, programming, and the cyber domain to effectively translate data into actionable insights, lead the analytic function during operations, and enable commanders’ decision-making. Designating the ASO role as a key developmental position appropriately acknowledges the ASO’s significant impact on the success of defensive cyberspace operations and signifies an important advancement for the Cyber Branch.”
A Long-Term Investment in Cyber Excellence
With this designation, the Army commits to systematically managing, developing, and retaining the specialized talent needed to confront evolving cyber threats. The move serves not only as a personnel management strategy but also as a reaffirmation of advanced analytics’ indispensable role in maintaining information dominance.
As cyber adversaries grow more sophisticated, the Army’s investment in cultivating a formidable analytic workforce ensures that the force remains resilient. The decision to classify ASOs as Key Developmental positions reinforces the ongoing priority on data-driven warfighting. This shift positions cyber operations at the heart of modern military strategy.
Story by MAJ Lindsay Roman
U.S. Army Cyber Command
MURFREESBORO, TN – The U.S. Army has announced that the MARS Inc, Barrett team has been selected as the winner of the xTech Soldier Lethality competition. In six months, this team of agile businesses were able to design, build, test, and demonstrate the effectiveness of a new 30mm grenade rifle system in support of the Army’s Precision Grenadier System (PGS) requirement. PGS is a soldier portable, shoulder fired, semi-automatic, magazine fed, integrated armament system (weapon, ammunition, fire control) that enables rapid, precision engagements to destroy personnel targets in defilade and Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) targets at close range. Both companies are proud to have the opportunity to provide this unique capability to the U.S. and allied war fighters.
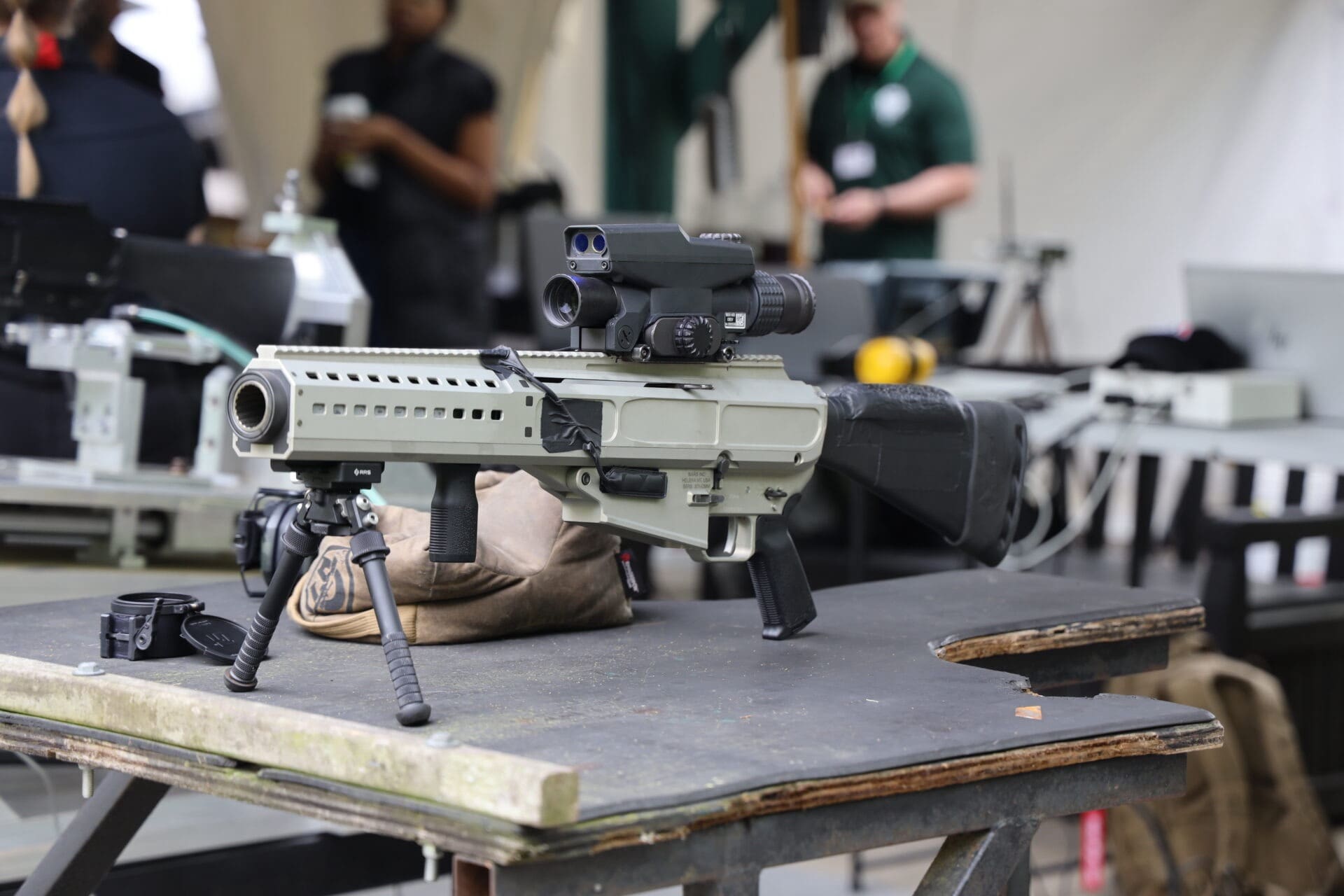

MARS Inc. and Barrett’s PGS submission for U.S. Army’s xTech.
“For decades, Barrett has changed the battlefield with revolutionary systems like the shoulder fired semi-automatic .50 caliber Model 82 and its modern variants, as well as the MRAD MK 22 — the world’s most accurate multi-caliber sniper rifle,” said Bryan James, Barrett CEO. “These weapon systems are now supporting the U.S. and more than 80 allied nations around the world. With our focus now on the U.S. Army’s PGS initiative, we are committed to delivering another game changing advantage: a system with Programmable Air Bursting counter defilade and Counter-UAS capabilities designed to keep our troops safe and ensure mission success.”
The xTech program was an incredible demonstration of the strength and capabilities of the Barrett team to collaborate with like minded companies to achieve what many thought unachievable in the given time frame. As part of that journey, Barrett worked closely with small business innovator MARS Inc to bring their technology to life, AMTEC Corp to develop an entirely new family of 30mm shoulder fired munitions, and Precision Targeting to provide a fire control system customized for the AMTEC ammunition. This new ammunition family will have the full spectrum of capabilities required to achieve the US Army’s mission to provide over match on the modern battlefield. This includes, Programmable Air Bursting High Explosive (HE), Proximity Fuzed and Point Detonating HE, as well as a Close Quarter Battle Round.
“This award highlights not only our technical capabilities, but the power of partnership, agility, and a shared mission,” said Ryan Krantz, Barrett Vice President of Business Development & Sales. “We’re proud to stand shoulder-to-shoulder with the U.S. Army to deliver the next leap forward in soldier lethality.”
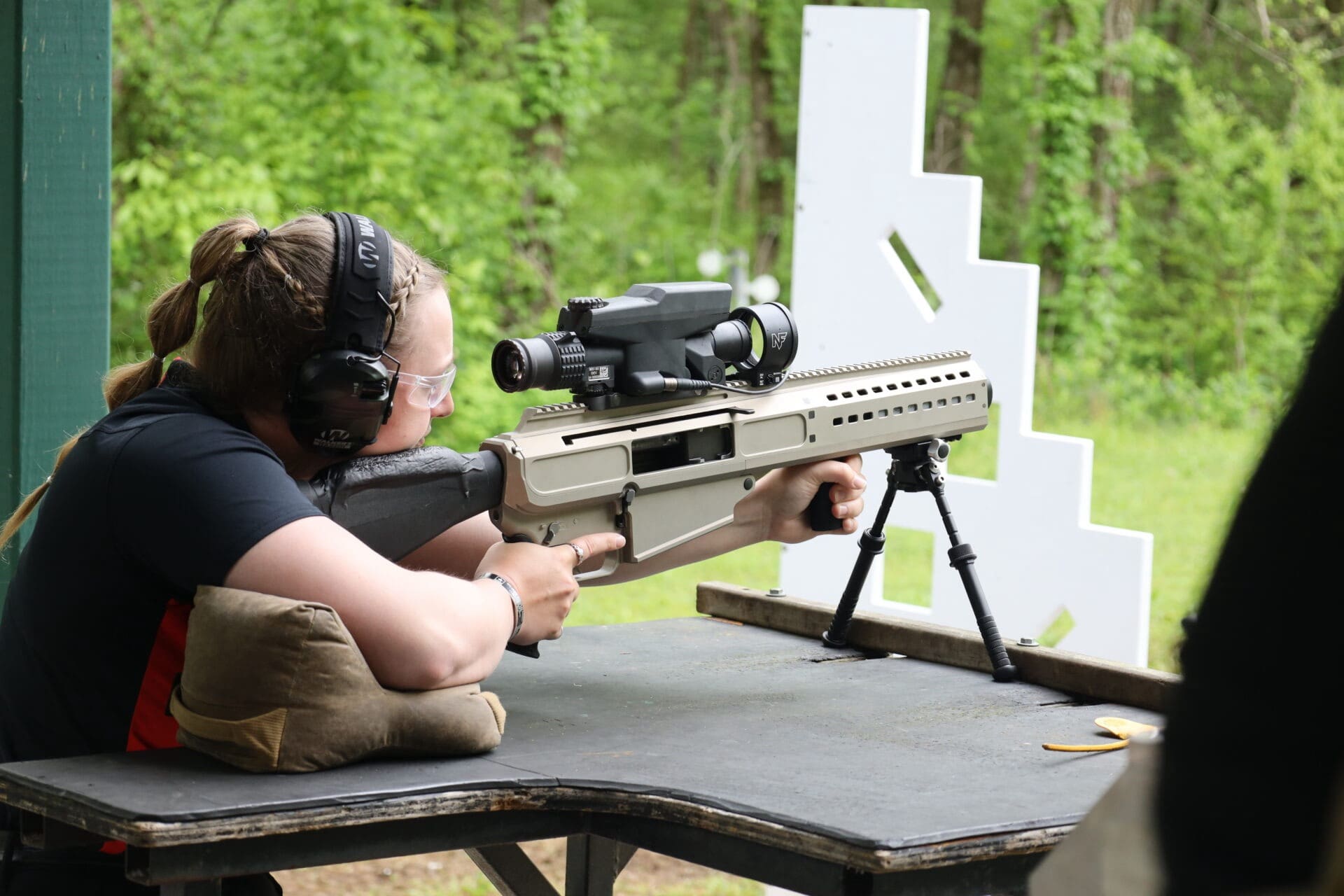

Barrett and MARS Inc. put their xTech Precision Grenadier System prototype to the test in a live fire event.