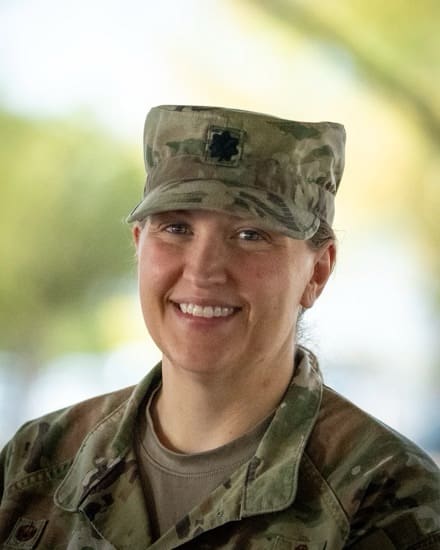
When Lt. Col. Sarah Bodenheimer, commander of the 355th Civil Engineer Squadron, was tasked with leading the Civil Engineering effort behind the Air Force’s Combat Air Base Squadron, there was no blueprint, only a concept. In less than a year, a first-of-its-kind unit had to be created from the ground up.
“We didn’t know what would work, but we knew we had to try,” Bodenheimer recalled. With no precedent to follow, she forged the way forward. “I made sure the team knew that the ‘do nothing’ course of action wasn’t an option.”
The CABS model brings together a cross-functional team spanning multiple specialties, all trained from the start to operate as one lean, agile, deployable element. “Traditional base operating support models weren’t built for the speed or posture demanded by today’s pacing threat,” Bodenheimer explained. “This unit is designed to project airpower from austere, contested environments quickly, independently, and with precision.”
Davis-Monthan Air Force Base, Arizona, was chosen to stand up the 11th CABS unit in 2024. As planning progressed, the team had to define structure, mission tasks, and readiness requirements. Establishing a dedicated CE CABS flight became the clearest path to meeting the demands of the new concept.
For Bodenheimer, the mission wasn’t just about building the structure, it was about empowering the people she led. Her role was to provide the ‘why’ and trust her team to execute, shouldering the institutional risk so they had the space to try, fail, and innovate. “If it’s successful, it’s all you. If something goes wrong, it’s all me,” she said. “I took this risk. I own it.”
She cultivated an environment where every Airman had a voice and a stake in the outcome—essential for blending individuals from different backgrounds and specialties into a cohesive team. Leadership wasn’t reserved for rank. “You don’t have to have all the answers to lead,” she emphasized. “Be honest, be clear about what matters, and don’t be afraid to make a call when others are frozen.”
Bodenheimer credits her parents with shaping the values that guide her leadership and work ethic. “They set the foundation: hard work, humility, and doing the right thing even when no one is watching.” She also comes from a family with deep military roots, including a grandfather in the Air Force, a grandfather in the Marines, and a Marine cousin who was critically wounded in Iraq.
That foundation was refined over the years by mentors, both in and out of uniform, who helped shape her leadership philosophy. “I’ve had leaders who taught me the importance of clarity, presence, and owning the impact you have on others,” she said. “At the end of the day, they all taught me to empower and take care of your people. Everything else will follow.”
Bodenheimer and her CE leads wrote new Concepts of Operations, established initial Standard Operating Procedures, identified training requirements, and navigated coordination with Major Commands and Combatant Commands stakeholders. She selected Airmen for the 11th CABS not just based on specialty, but on mindset and potential, forming a team with a balance of technical expertise and leadership capacity. Many junior members stepped into leadership roles for the first time—and delivered.
Standing up the unit also meant pulling 48 personnel from the 355th Civil Engineer Squadron, all while daily operations at Davis-Monthan continued without pause. Those who remained shouldered the extra weight, and it was important to Bodenheimer that they knew their work was essential to the larger mission. “That kind of quiet excellence often gets overlooked,” she noted. “But not by me.”
For Bodenheimer, success wasn’t measured by perfection, but by progress. Looking ahead, she doesn’t see what they built as a finished product, but as the beginning of something larger. “Are we getting it perfect? Who knows,” she said. “But I know the 355th CES Airmen on that team are doing everything they can to find a path and lead the way.”
She also views the effort as a long-term commitment to the CE enterprise and to the future of deployed operations. “I believe deeply in CE’s role as an enabler of airpower,” Bodenheimer emphasized. “Getting this right meant giving the Air Force a credible, deployable solution for base ops in the pacing threat environment. It also meant getting it right for our future CE Airmen who will be on the front lines of the next conflict. That mattered.”
Bodenheimer hopes that when all is said and done, her Airmen remember that she had their back. That she expected a lot but gave just as much. And, that she cared about the mission, but cared more about the people doing it. “I pushed them to lead boldly and think bigger because they’re capable of more than they realize.”
The construct of CABS will continue to evolve. The people may change, and the structure may shift. But when there was no blueprint, Bodenheimer helped draw the first lines and ensured her team had the trust, clarity, and support needed to succeed.
“We didn’t just prove the concept, we made it operational,” Bodenheimer said proudly. “We took theory and turned it into reality.”
Story by Alexandra Broughton
Headquarters Air Force, Office of the Director of Civil Engineers