Photo: SPC Dustin D. Biven, 22nd Mobile Public Affairs Detachment
Since 2001, the Common Access Card, or CAC, has served as the de facto, government-wide standard for network and system security access control. However, CAC cards are not operationally suited for use in every environment.
Moreover, the Army lacks a standard way for Soldiers at every echelon to prove their identity when operating systems, devices and applications on Army networks.
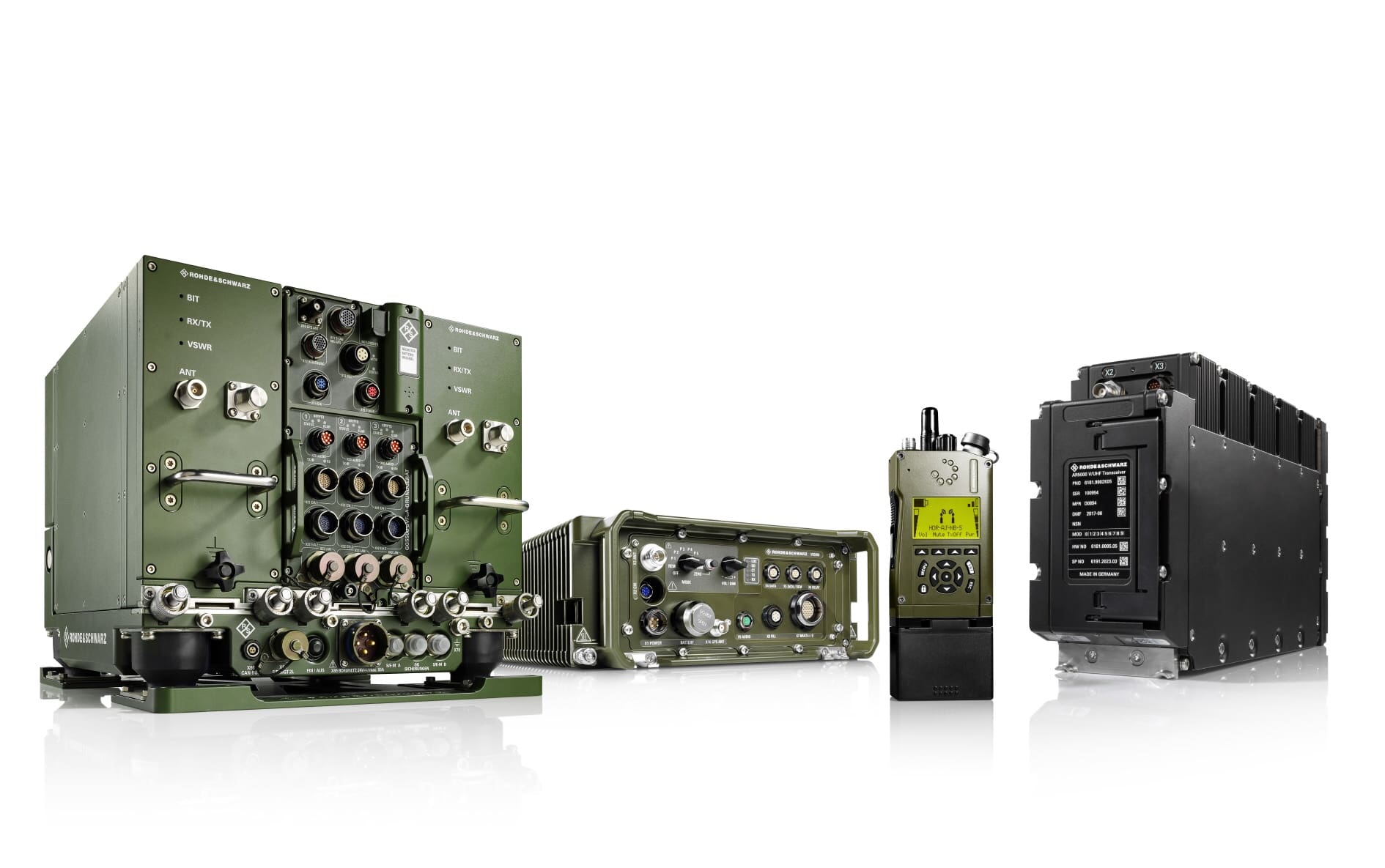
With this in mind, AFC’s major subordinate command, the U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command, or CCDC, is researching and developing authentication technologies that will provide Soldiers with secure and simple ways to identify, authenticate and be authorized access to Army networks, operating systems, servers, laptops, applications, web services, radios, weapon systems and handheld devices.

Photo: Combat Camera, courtesy of CCDC C5ISR Center public affairs
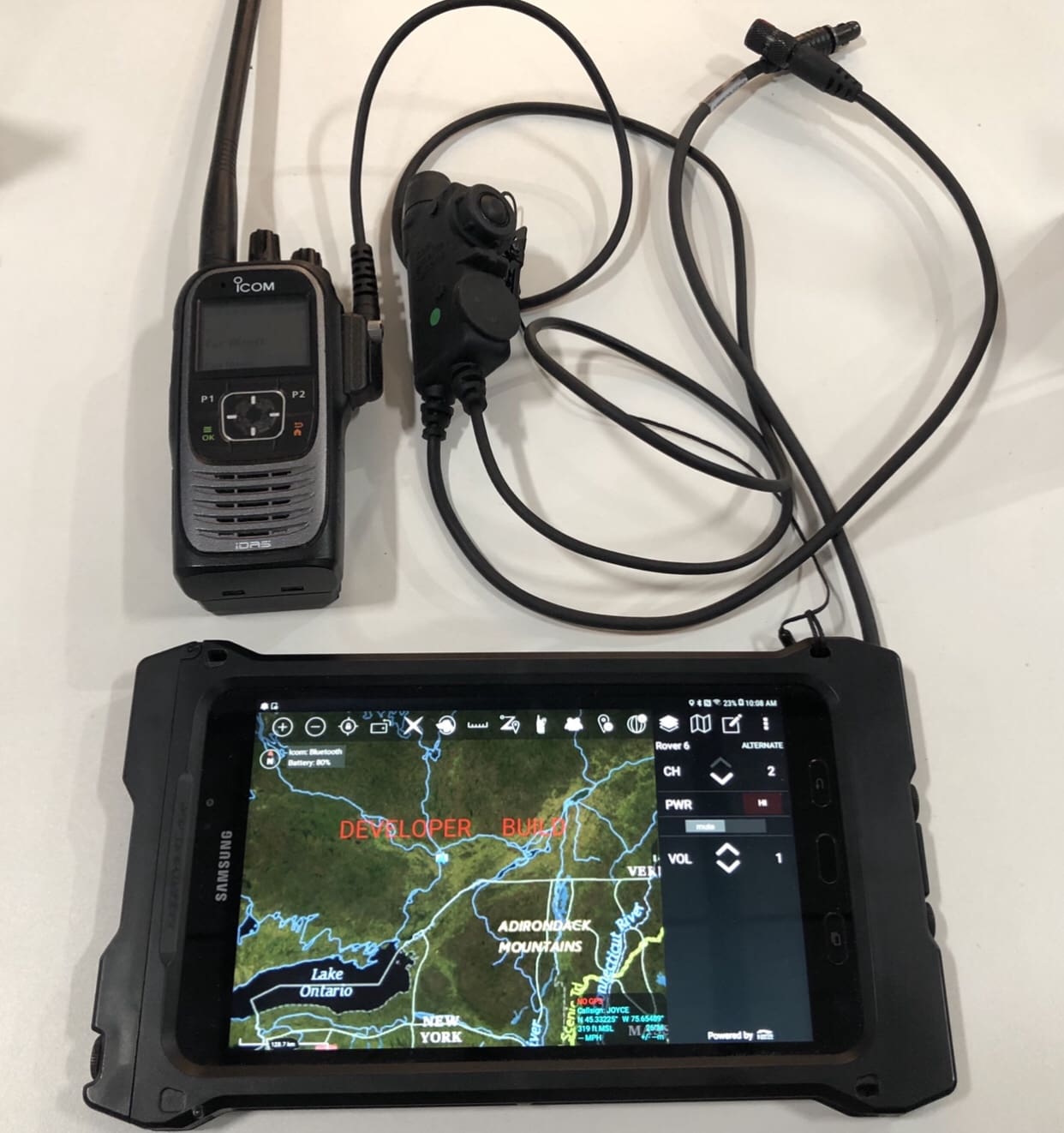
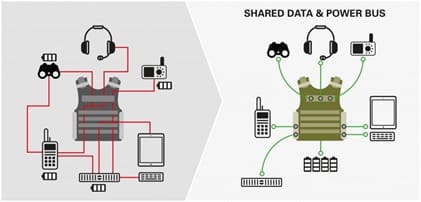
CCDC’s Command, Control, Communications, Computers, Cyber, Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance, or C5ISR, Center is designing wearable identity tokens for Soldiers to use to log on to mission command systems, networks and tactical platforms. The tokens are wireless, lightweight, flexible and rugged, and they can be inserted in a Soldier’s pocket, attached to a sleeve or integrated into a wrist band like a Fitbit.
Conceptually, Soldiers wearing these tokens could simply approach a system to login, be recognized by that system, which would then prompt the Soldier to enter a PIN or use a biometric as a second factor, and be automatically logged out when they walk out of the system’s range.
“The Army is driving towards a simpler and intuitive tactical network, so we’re aligning our Science and Technology resources to explore the challenges associated with this mission space, inform senior decision makers of the lessons learned and deliver capabilities that support Army Modernization and address the Soldier’s needs — now and in the future,” said Brian Dempsey, Tactical Network Protection chief for the C5ISR Center’s Space and Terrestrial Communications Directorate, or S&TCD.

Photo: Douglas Scott
The wearable identity tokens combine the security of a public key-based credential — similar to the credential on the CAC — with cutting-edge advances in the commercial wireless payment industry and flexible hybrid electronics, explained Ogedi Okwudishu, project lead for the Tactical Identity and Access Management, or TIDAM, program.
“As part of the Army Futures Command, we’re looking to move at the speed of the information age. We want to be able to research, test, proof the concepts and integrate emerging IT capabilities from industry as they become available. There’s no point re-inventing the wheel,” Okwudishu said.
Under the current paradigm, tactical platforms would need to be retrofitted with specialized equipment in order to read new identity authentication technologies. Such deployments and retrofitting can be very costly. Wearable tokens, however, leverage already existing communication and protocol capabilities, Okwudishu pointed out.
“Soldiers should not have to take out a smartcard, insert it into a card reader and then remember to remove the card from the reader when they are done,” said Okwudishu. “Contactless identity tokens are not only easy to use, they provide a significant cost savings for the Army. You can continue to add authentication capabilities without needing to redesign, or deploy new, tactical hardware to every laptop, server, handheld device or weapon system in the field.”
Since beginning the TIDAM program in 2017, the C5ISR Center has worked closely with Soldiers and Program Executive Offices, or PEOs, Soldier and Command, Control Communications-Tactical, or C3T, to validate, demonstrate and mature the technology.
The center’s S&TCD is working with Project Manager Integrated Visual Augmentation System, or IVAS, to finalize a transition agreement with PEO Soldier for wearable authenticator infrastructure technologies. In the meantime, the directorate is developing a wearable authenticator software provisioner that will enable the secure placement of credentials on the wearable tokens and the ability to do this “locally” at the brigade level and below.
S&TCD is also working from a roadmap it jointly developed with PEO Soldier to integrate the capability with various systems from PEO Soldier and PEO C3T. Currently, the goal for fielding the tokens is in FY 22.
“I think this is a really great idea,” said Sgt. 1st Class David Worthington, senior enlisted advisor for the C5ISR Center. “Nobody has done anything like this yet. If done properly, it will make the authentication process a lot easier and a lot faster. More important, it provides more reciprocity at the tactical level for log-ins, so you can track what people are doing on the network.”
By Douglas Scott