CAMP GRAYLING, Mich.—In modern warfare, battles are not only fought with rifles, tanks and artillery. Some of the most decisive victories are won across the electromagnetic spectrum.

At Northern Strike, the National Guard’s premier readiness exercise held this month at Michigan’s National All-Domain Warfighting Center, Soldiers trained in a high-intensity environment that pushed the limits of electromagnetic warfare, or EW. It tested their skills in realistic combat scenarios.
In classrooms, electromagnetic warfare specialists often train to disrupt, or “jam,” enemy communications, intercept signals and scan for threats. Jamming works by overpowering or confusing an enemy’s radio or data transmissions, preventing them from communicating or coordinating effectively.
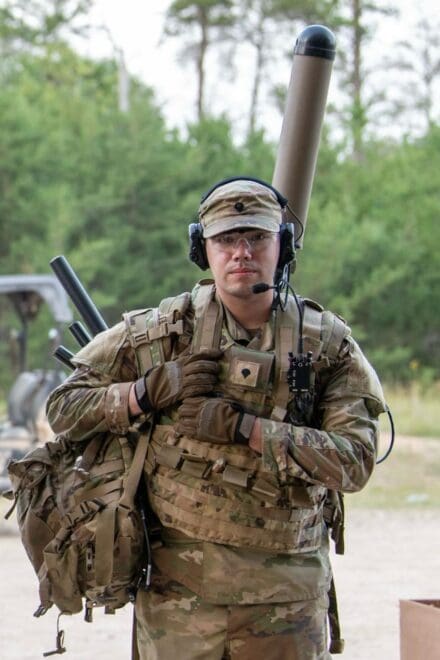

Last year at Northern Strike, the 37th Infantry Brigade Combat Team, or IBCT, launched a pilot program that sent a mobile EW team into the field to disrupt the communication systems of units in training.
This year, the EW teams were embedded in infantry squads to create a more realistic, complex environment for Soldiers.
“This is a rare training opportunity in the National Guard and in the Army as a whole,” said Spc. Robert Bowley, an Electromagnetic Warfare specialist in the 37th IBCT from Columbus, Ohio. “To train with the equipment, you need the funding, and Northern Strike allows for that.”

Bowley was equipped with the Beast+ system, a handheld multi-channel receiver and transmitter designed for Army EW operations. The system scans the electromagnetic spectrum to detect enemy signals, identify spoofing or jamming threats and enhance battlefield awareness.
“The antenna gives you a general direction and signal strength. I can see anything on the [radio frequency] spectrum,” Bowley said. “We also have a power amplifier that lets us jam communication systems.”
Bowley, who also participated in the exercise in 2024, said he acted as “an early warning system. I will be giving the direction of the opposing force and jamming their comms.”

The mission brought together electromagnetic service members from the 37th IBCT, the Royal Irish Regiment and the Latvian National Armed Forces. The teams combined their expertise by embedding an electromagnetic specialist with the Irish regiment and managing signal towers with the Latvian forces to carry out a complex, coordinated operation.
“In my job, you are on the front lines. We are not cyber on computers, we are in the field,” Bowley said.
At 1800 hours, Browley and seven infantry soldiers from the 2nd Battalion, Royal Irish Regiment, British Army, stepped off to the Combined Arms Collective Training Facility, which simulates fighting in urban terrain. Once they arrived, the squad cleared the building and Bowley looked for the best place to set up the Beast+.
“Ideally, it would be on top of a roof,” he said. “But they have drone capabilities, so this [his location] was the next best thing. In the best case scenario you want to be high up and have nothing around you.”
While the Royal Irish Regiment placed obstacles around the building, Bowley found a dark corner with windows on both sides.
“We will be defending from up here. With this spot, I have a window on both sides and am able to get the antenna outside. The main thing that is important is what is being said over the radio. When I see something on my screen, I will know the direction they’re coming from,” Bowley said.
Bowley knew the long night ahead would test his focus. He monitored the electromagnetic spectrum for hours, watching for the slightest signal of an attack and standing ready to jam enemy communications.
“I brought a lot of caffeine,” he said, laughing. “We have the go-ahead to jam whatever. Usually, you have to really go through hoops. The problem with jamming is that it is risky. Turning off comms can do a lot. The things that I will be looking at jamming are important. Like when they call up nine-lines, or before an assault.”
Bowley’s squad was on defense, which required members to stay alert the entire time. At 2200 hours, they experienced probing from a platoon-sized element testing their defenses. A drone tagged four simulated casualties.
At 0300 hours, shouts echoed as infantry teams moved in to assault the objective. With their communications jammed, the attackers yelled to coordinate.
“They realized we were jamming them and immediately got off their comms,” Bowley said.
Moments later, the opposing force stormed into the room and took down the defending squad in the exercise.
Master Sgt. Jason Ross, the electromagnetic spectrum operations noncommissioned officer for the Army National Guard Information Advantage Division, said the exercise was a reminder of why electromagnetic warfare must be integrated into training.
“Communications systems have changed rapidly in recent years and now evolve almost monthly,” Ross said. “The threat has grown significantly. Thinking outside the box is critical, but it’s not always an easy discussion to have.”
This scenario was unique because the communications cell was on the red team, creating an unpredictable training environment.
“It is hard to duplicate what we are doing at Northern Strike. The approval for this type of training is tricky. The support that Michigan has given to this exercise is amazing,” Gilly said. “The reality is when we train on a rifle range, a Soldier knows what to expect. That is not the case with electromagnetic warfare.”
Maj. Tucker Palmatier, a cyber electromagnetic warfare officer and Cyber Electromagnetic Activities officer in charge of the 37th Infantry Brigade Combat Team, said training in electromagnetic warfare is challenging because of federal restrictions.
“The FCC [Federal Communications Commission] law on jamming dates back to 1934, which makes it difficult to realistically train for today’s technology-driven battlefield,” Palmatier said.“Our challenge is maximizing training opportunities without breaking laws or regulations so Soldiers know exactly what to expect when it matters most.”
Despite those hurdles, Palmatier said the operation was a success.
“Our enemy was not anticipating electromagnetic warfare. We were able to degrade their communications, which left them unable to coordinate their attack, allowing a smaller force to successfully defend the position,” he said.
By 2LT Paige Bodine, Michigan National Guard