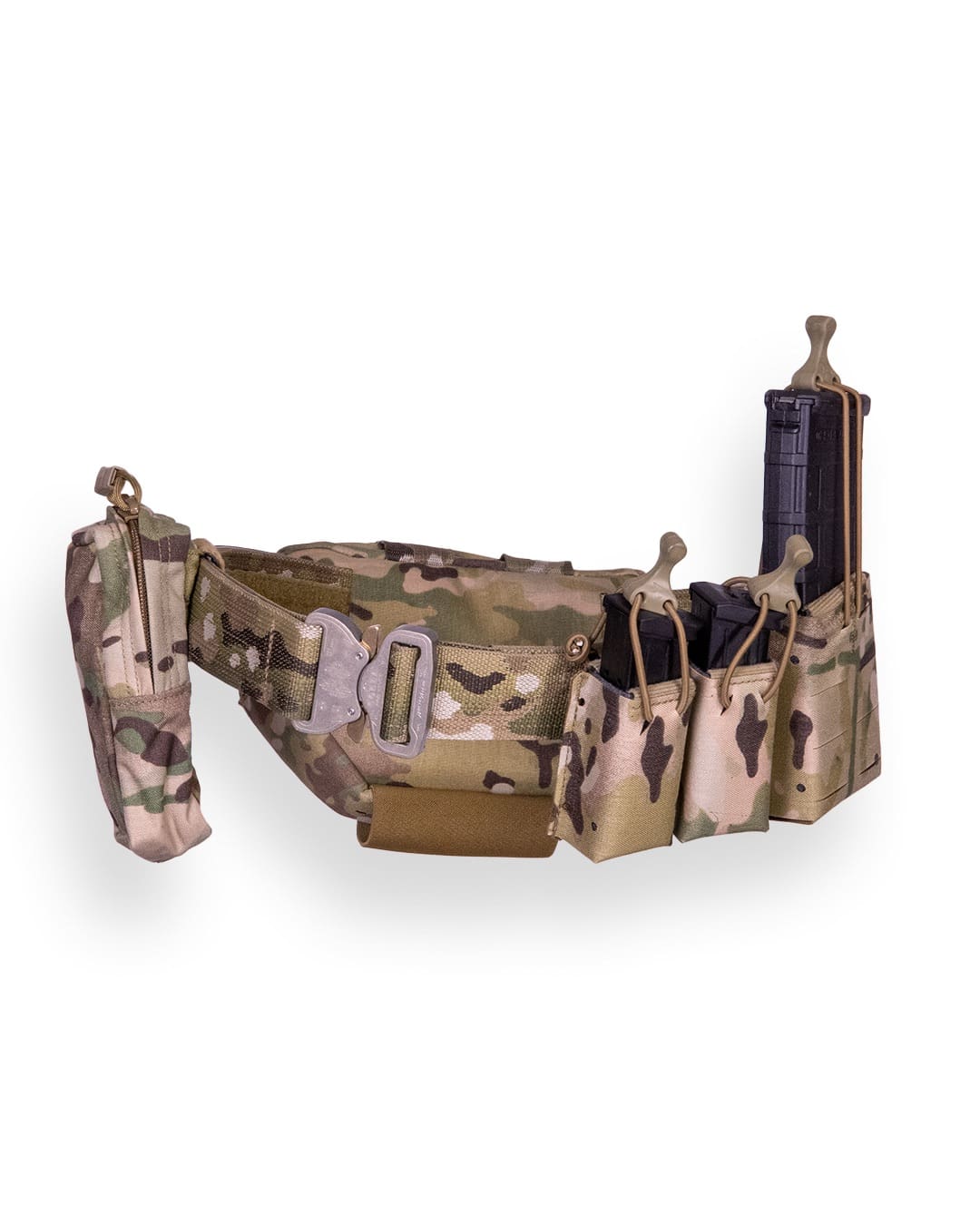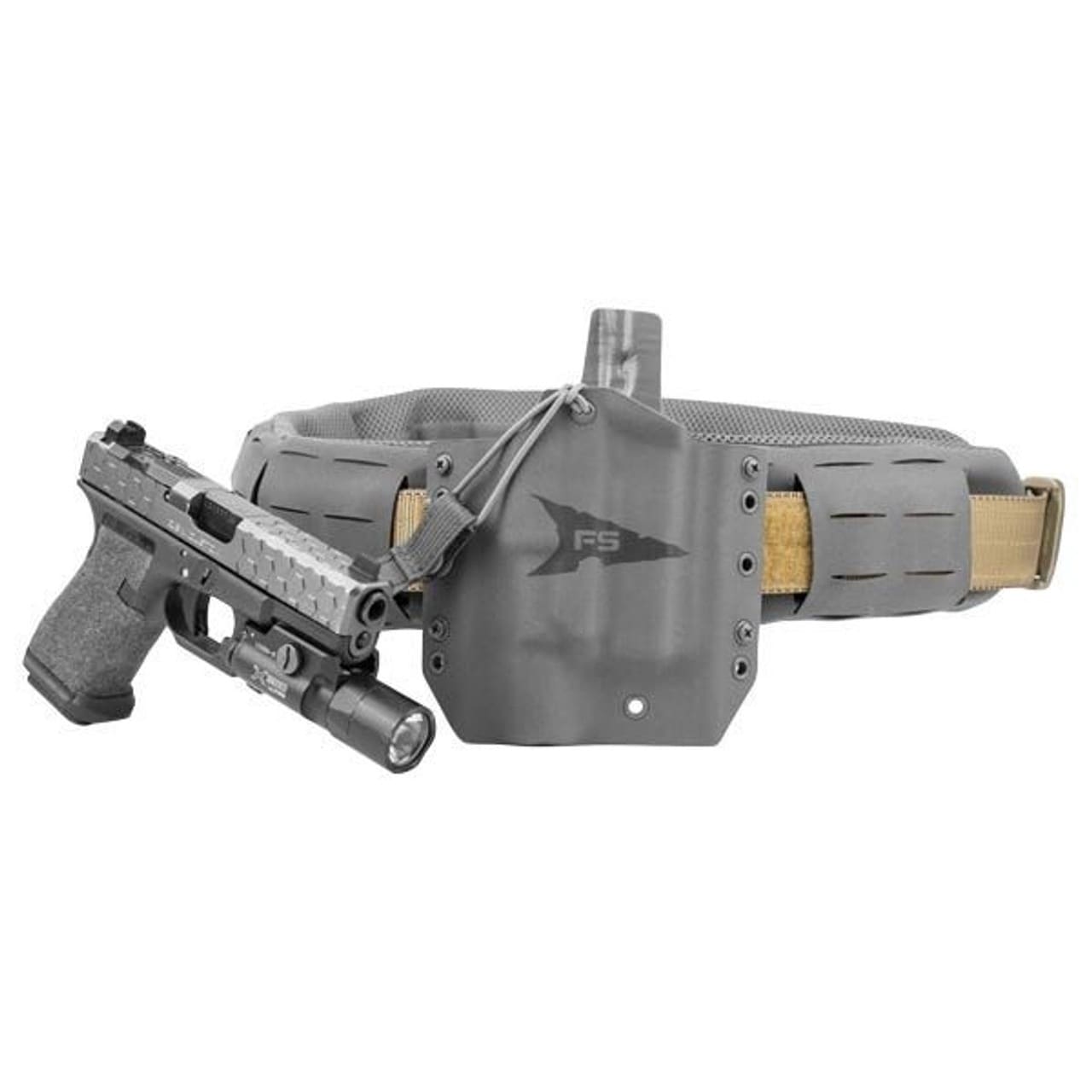
Managing two to three casualties in the real world from a first-line aid bag is not an ultralight solution in the modern age of DCR and Blood Cold Chain. There is an argument to be made that light and fast is an advantage, which is valid, but “heavier” often equals more capable (a Role 2 is more capable than POI, etc). That’s not to say bring the kitchen sink to the POI, just that efficiencies must be incorporated into the first-line bag to adhere to the standard of care, which includes carrying LTOWB (Low-Titer O neg Whole Blood).
As protocols evolve, medics are asked to perform more tasks during Damage Control Resuscitation (DCR) at the Point of Injury. Due to advances in medical research that have driven protocols over the past 20 years, there is no choice but to increase the average Liter size of the first-line aid bag.
To optimize the most current standard, the two-unit SOP, we have developed a stand-alone aid bag that breaks a few barriers.

Overview of DCR
To understand why the first-line aid bag design must evolve, it’s essential to define the operational challenges it faces. Effective DCR in the field requires maximizing efficiency and minimizing time to treatment. Medics are now expected to perform tasks that entire teams in Level 1 trauma centers often struggle to execute under controlled conditions.
DCR at the Point of Injury includes:
- Mastery of TCCC fundamentals
- Employing LTOWB at the point of injury, including cold-chain transport and blood warmers
- Administering POI medications such as TXA and calcium
- An advanced understanding of acute traumatic physiology to manage hemorrhage, optimize resuscitation, and mitigate shock, coagulopathy, and hypocalcemia
M9 Aidbag
Legacy products like the M9 bag paved the way for modern systems, which explains their longevity. But twenty years is a lifetime in this industry– and the M9 is showing its age. It’s heavy for its size (due to outdated construction), inefficient for modern resuscitation (it lacks the capacity to carry 2U of blood), and constrained by space in the main compartment. In short, it no longer meets modern requirements.
What follows is the result of years of advancement in design, manufacturing techniques, and application of DCR principles at the point of injury.

Figure A. M9 vs. CRO 26L: Larger capacity, improved ergonomics, and purpose-built for DCR.
Our design philosophy is to maximize durability without unnecessary bulk– every medic remembers carrying “bomb-proof” gear that is far heavier than it needed to be (ie, STOMP bag).
We use modern materials and construction techniques. By utilizing double-stitch seams and eliminating excess fabric in the name of “strength,” we achieve a lighter product that is equally as “bomb-proof” as legacy milspec standards. This includes removing all edge bindings, doubling as a weight saver with visible workmanship (not hiding sloppy sewing).
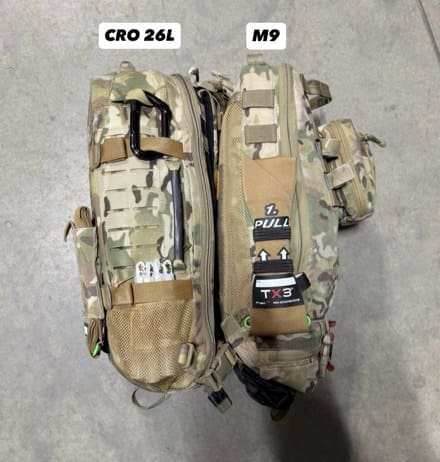

Figure B. Increased depth improves closure and eliminates the need for supplementary external pouches.
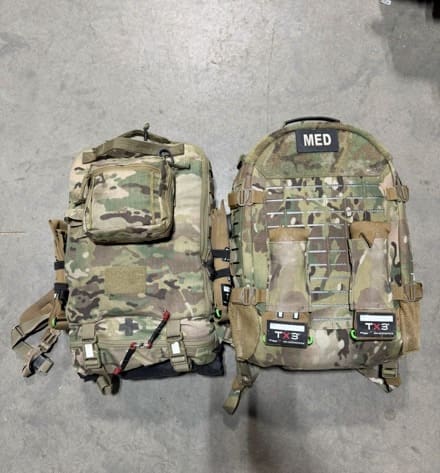

Figure C. M9 vs CRO DCR 26L
CRO 26L Aid Bag
The CRO 26L represents a deliberate step toward the ultimate goal: fitting all required resuscitation equipment for 2-3 combat wounded (an M9 bag equivalent) into a first-line bag capable of carrying two units of blood, and scaling to Prolonged Casualty Care setups (vents, monitors, etc.). It replaces the RATS pack capacity with a fraction of the offset from the body and offers much better space utilization.
Specifications:
- Chassis-opening design
- Weight: 3.8 lb (Empty RATS: 8 lb for comparison)
- Volume: 26L
- Removable waist strap (no hip pads)
- Adjustable shoulder straps
- Chest strap
- Lightweight adjustable chassis
- Customizable interior loop field
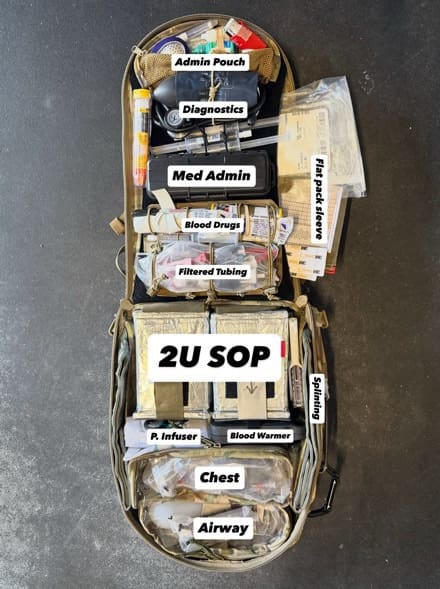
Figure D. Chassis-opening, complete workstation, optimized for custom organization of resuscitative equipment plus two units LTOWB
Chassis-Opening
This feature is, to our knowledge, first-in-industry. After observing countless trauma lanes, most modern DCR-focused medics primarily work off their belt, making an effort not to drop their aid bag unless the patient needs to be resuscitated with blood. The chassis-opening feature eliminates the need to flip the bag over to access the main compartment. Something that seems so minor is one of the main features gaining attention from our user base.
Combined with its weight, capacity, and configurability, the 26L is designed to support best practices in DCR, including whole-blood resuscitation at the point of injury.

Thank you for your community engagement on this project and for supporting our mission to innovate medical equipment and improve treatment protocols to enable faster, more capable medics.
If you have questions or would like a quote, email us at support@cromedical.com at





































































































































