The ongoing war in Ukraine has demonstrated the deadly efficiency of modern battlefield targeting. Rapid sensor-to-shooter integration, enabled by signals intelligence (SIGINT), geospatial intelligence (GEOINT), and unmanned aerial systems (UAS) reconnaissance, has shortened kill chains to the point where detection often leads to immediate engagement. High-value assets, identified through electronic emissions or ground-based reconnaissance, face a severe risk of engagement and destruction. The prevalence of SIGINT collection, integration of UAS, and massed indirect fires in the doctrines of American adversaries represents a complex problem that can be mitigated by the use of tactical deception.1
Russia and China both employ multi-layered information collection and rapid sensor-to-shooter systems. Command and Control (C2) nodes are an example of High-Value-Targets (HVT) targeted by adversary doctrines and are a convenient example for exploring the use of, and opportunities created by, deception. Adversary doctrine describes the following kill chain for engaging C2 nodes: mobile SIGINT collectors locate command nodes, UAS confirm the target location, and artillery at echelon execute massed fires strikes before blue force commanders can react. The threat to U.S. forces this system represents is not theoretical, it unfolds daily on the battlefields of Ukraine and represents the conditions under which American forces are expected to fight and win. These doctrines are replicated every rotation at the National Training Center (NTC), where the Troopers of the 11th Armored Cavalry Regiment (Blackhorse) serve as the professional opposing force (OPFOR). Blackhorse provides units with a critical opportunity to train against the techniques America’s adversaries use daily. Unexercised solutions already exist within Army formations to mitigate the effects of the modern battlefield’s shortened kill chains. By understanding adversary collection techniques, reducing signature, and presenting deception signatures, battalions can disrupt enemy targeting cycles and create opportunities for lethal response.
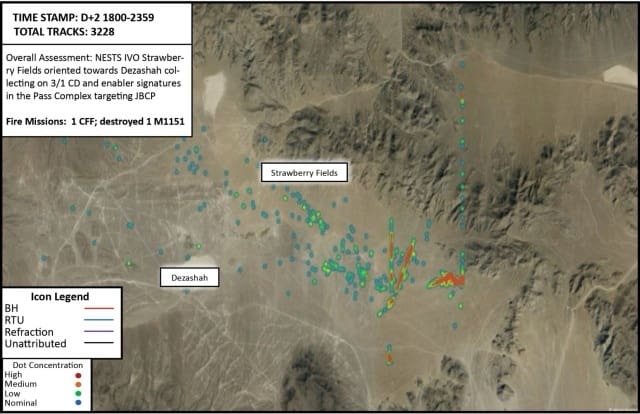
Figure 1. NESTS in the vicinity of Strawberry Fields oriented towards Dazashah collecting on rotational brigade MCP and enabler signatures in the Pass Complex targeting Joint Battle Command-Platform (Photo by 11th ACR Regimental S2)
Threat Collection Doctrine
Russia and China prioritize rapid target acquisition, integrated information collection, and fire control automation as core tenets of their military doctrine. The 7-100 series doctrinal manuals lay out their shared approach to large-scale combat operations (LSCO), detailing the reliance on multi-layered information collection systems that feed directly into massed indirect fires, shortening the time between detection and engagement. SIGINT plays a critical role in this process, by geolocating friendly forces C2 nodes and tracking emissions from communications and mission command information systems. GEOINT, collected by UAS, supplements SIGINT data by confirming target locations and conducting battle damage assessment (BDA) to refine follow-on strikes. This integrated targeting process ensures that friendly forces are rapidly engaged before they can reposition, react, or conceal themselves.
For U.S. forces, the threat posed by this level of collection and targeting cannot be overstated because of our reliance on digital mission command systems. The ability of adversaries to rapidly detect and engage formations means that any electronic emissions or movement bears significant risk of compromise and targeting. Without effective mitigation measures, units risk being outpaced in the decision-making cycle, allowing the enemy to dictate the tempo of battle. Blackhorse replicates these conditions at NTC, ensuring that rotational training units (RTUs) experience the same information-driven targeting process they will face in combat. By understanding how adversaries collect and process information, U.S. forces can better prepare to disrupt, degrade, deny enemy kill chains.
Threat Replication
Blackhorse executes information collection operations by integrating SIGINT, UAS, and ground-based reconnaissance to target friendly command and control C2 nodes, thereby disrupting decision-making processes. Their layered sensor network operates in a sequence designed to detect, validate, and engage targets in real time. The Networked Electronic Support Threat Sensors (NESTS) system collects SIGINT, identifying emissions from satellite-based communications, while the Versatile Radio Observation and Direction (VROD) system intercepts frequency modulated (FM) transmissions to locate and classify targets. Identification of likely targets by SIGINT cues UAS to confirm targeting data and refine collection. Due to limited time on station, UAS only remain on their assigned named areas of interest (NAIs) long enough to confirm targeting data before moving on to identify additional targets in support of the maneuver fight. Small UAS (sUAS) may conduct BDA later if required.
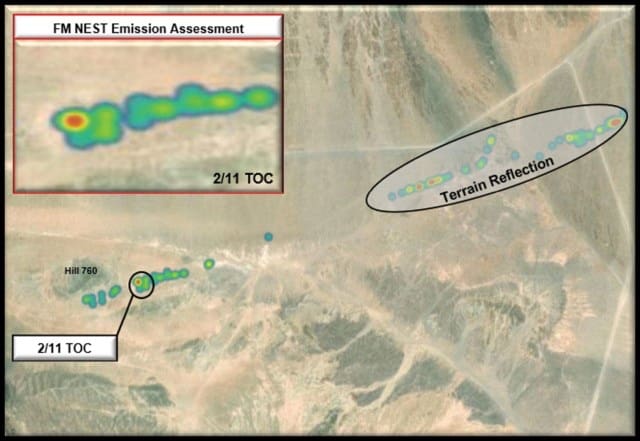
Figure 2. FM NEST Emission Assessment for 2/11 TOC (Photo by 11th ACR Regimental S2)
Once validated, the Blackhorse Regimental Targeting Intelligence Cell (RTIC) processes the refined target data and passes it to fires elements for strike execution. This sensor-to-shooter process mirrors adversary workflows, where electronic detection leads to physical compromise and rapid engagement. The effectiveness of this process underscores the necessity for signature management, deception, and counter-fire strategies to disrupt enemy kill chains.
Defeat through Deception
Deception is a fundamental aspect of modern warfare but is typically relegated to a survivability operation. Successful battlefield deception forces adversaries to misallocate resources, delay decision-making, and strike false targets. FM 3-90 defines deception as actions executed to deliberately mislead adversary decision-makers about friendly military capabilities, intentions, and operations.2
Adversary intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) networks rely on rapid detection, classification, and engagement. By integrating deception, friendly forces can manipulate enemy perception, disrupt targeting cycles, and increase survivability.3&4
Deception operates across all domains and targets two specific dimension: physical and technical. Together these dimensions influence the cognitive, or human, dimension of decision making. Physical deception uses false positions and decoys to mislead enemy analysts into assessing a decoy as a legitimate target. Technical deception manipulates the electromagnetic spectrum (EMS) by emitting signals that mimic actual targets, causing adversary collectors to misinterpret the data. C2 nodes have both a physical and technical signature, making them a useful example for exploring the requirements of a deception story.5
Units generate deception stories by creating signatures inside the collected spectrums, that force adversary analysts to make false assessments. In the electronic spectrum, the deception node must emit signatures that mimic a C2 node. This requires units to allocate FM and Joint Battle Command-Platform (JBCP) capability to the deception node as both systems are present in MCPs. JBCPs constantly update their location data to the network, creating a continuous low-power emission. JBCP emissions are commonly assumed to be too weak to be detected, this is a false assumption. In addition to being detectable, the static nature of C2 nodes allows enemy analysts to accurately classify their emissions as a C2 node and initiate a queuing cycle and kill chain.
Reinforcing the deception story requires physically constructing the deception node to present a believable target. After SIGINT assets identify a likely MCP, adversary doctrine calls for UAS or ground reconnaissance to validate the target. Blackhorse replicates this effect with a dedicated MQ-1C Gray Eagle during NTC rotations. When UAS collection begins, the deception node must match the physical signature of an actual MCP. To achieve this, units must equip the deception node with wheeled vehicles, tentage, antennas, and other identifiable MCP-associated equipment.
Battalions can improve deception effectiveness by creating deception kits from non-functional or excess equipment components. Broken antennas simulate active communication architecture, while trailers transporting generator mockups and fuel cans replicate life support systems. Worn-out power cables present the image of power distribution to tents, reinforcing the illusion of an operational command node. Because high quality thermal sensors are widely available common commercial markets, the deception node should also mimic the thermal signature of an operational command node. Crews can simulate a generator’s thermal signature by piping exhaust from the towing vehicle into the decoy, allowing it to escape through a replicated exhaust port. Properly routing exhaust tubing and covering both the vehicle and the fake generator with camouflage netting obscures the deception and breaks up its physical signature, making identification of the deception story as a deception less likely. Damaged shelters staged as command post structures further reinforce the deception story without risking mission-essential assets. Integrating these elements allows units to construct deception nodes capable of withstanding both SIGINT and GEOINT validation.
To reduce risk, all personnel should withdraw from the deception node once it establishes. A technique to improve the deception teams survivability is to locate them in offset security positions, several hundred meters away, minimizing exposure while maintaining operational control of the node. Using wired connections to FM radios enables deception teams to transmit from secure positions, increasing the deception node’s electromagnetic (EM) signature while keeping personnel protected. This method strengthens deception by making the site appear active while preserving force survivability. Another technique to strengthen technical deception is to equip the deception node with a CX-13298 Retrans Cable, commonly known as a “dog bone”. This cable allows the deception node to act as a retrans site, mimicking the radio traffic of the actual C2 node while simultaneously allowing the C2 node to broadcast lower power transmissions, reducing the likelihood of electronic detection.
The final step in any deception operation is concealing the actual asset. While the deception nodes attract enemy collection by design, the real MCP must obscure or eliminate the signatures that would expose its location. This requires reversing the techniques used to make the deception node appear authentic and ensuring the protected asset remains undetected.
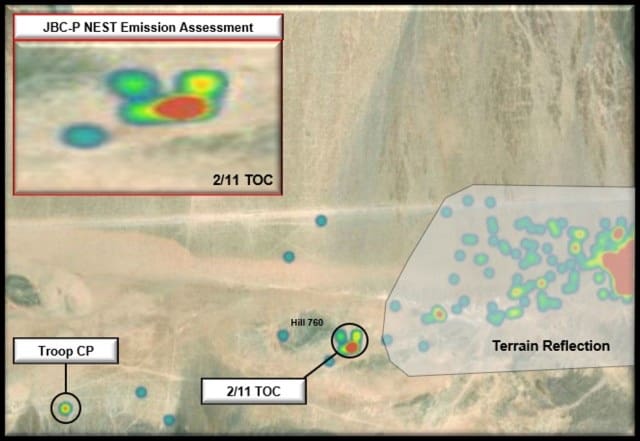
Figure 3. JBC-P NEST Emission Assessment for Troop CP and 2/11 TOC (Photo by 11th ACR Regimental S2)
Minimizing electromagnetic emissions is the first priority. JBCP should operate on communications windows, establish offset from the MCP, or establish behind terrain that completely masks horizontal emissions. FM radios should connect by hardline to an offset antenna farm, preventing immediate correlation between transmissions and the MCP’s physical location. ATP 6-02.53, “Techniques for Tactical Radio Operations,” details how antennas can offset more than two miles using ASIP remote operations via hardline connection, reducing the MCP’s exposure to SIGINT collection.6 When using a retrans setup on the deception node, the C2 node can locate in terrain that masks FM communication forward but allows broadcasts to hit the retrans system. These techniques not only improve concealment but also reinforce the deception story by generating EM emissions at the decoy location.
Beyond SIGINT mitigation, the physical composition of the MCP should be structured to blend into the operational environment while still meeting operational requirements. Use of vehicles and equipment incongruent with an MCP, reducing the size of the node, and collapsing assets during periods of UAS reconnaissance all contribute to the deception story by representing the C2 node as a different asset.
Reports of contact with UAS should trigger protection battle drills, including breaking down easily identifiable equipment, applying additional camouflage, or even jumping the command post to prevent the presentation of an easy target. Once the ISR threat is neutralized or off-station, units can restore digital communications as needed.
Leveraging Lethality from Deception
A well-integrated deception plan must align with counter-reconnaissance, fires, and intelligence planning, anticipating how and when enemy collection assets will react, and how to actively counter their efforts. This concept is rooted in reflexive control, a strategy developed by the Soviet Union in the 1960s and 1970s. Reflexive control seeks to manipulate an adversary’s decision-making process by shaping their perception, leading them to take actions that are predictable and favorable to the initiator. In this context, deception forces the enemy into a predictable reaction, which friendly forces can prepare to exploit.
Given the passive nature of SIGINT collection, the first engagement window occurs when enemy UAS attempts to validate the deception target. To counter this, units should establish anti-air ambushes near MCPs and deception nodes, positioning short-range air defense (SHORAD) or mobile air defense teams in ISR flight corridors. This allows friendly forces to engage enemy ISR platforms before they collect actionable intelligence, denying the enemy the ability to confirm or refine targets.
If the enemy cannot validate the target with UAS, they may deploy ground reconnaissance teams to confirm or deny its presence. By identifying and securing ground infiltration routes, units deny the enemy access to the deception node, reinforcing the perception that a high-value target is present while creating opportunities to trap and destroy enemy reconnaissance elements before they can collect.
If deception is successful, the enemy will likely commit fires assets against the deception node without validation, encouraged in their belief that these protective efforts are aligned against a real asset. The final engagement opportunity, where counter-fire radar, ground moving target indicator (GMTI) radar, and national level collection can detect and track enemy fires assets that have unmasked for a valueless engagement. Friendly forces can track and destroy these targets, preventing their use against friendly forces and creating hesitation to unmask assets for future strikes.
By integrating deception with air defense, counter-reconnaissance, and counter-fire operations, units can force the enemy into predictable, exploitable mistakes while preserving their own combat power. Deception is not passive. It is a deliberate operation that includes all warfighting functions and sets conditions for the enemy to fail.7
Conclusion
By understanding adversary collection techniques, reducing the signature of high-value targets, and leveraging deception to shape enemy behavior, units can force adversaries to misallocate ISR and fires assets, disrupting their kill chain and protecting friendly forces. Current conflicts are occurring in highly contested ISR environments, where failure to integrate deception will result in rapid targeting and engagement.
Deception is not just a defensive tool, it shapes the battlefield by forcing adversaries to react to false information, creating opportunities to disrupt their targeting cycles and degrade their effectiveness. A well-integrated deception plan must synchronize with reconnaissance, fires, and intelligence planning to maximize survivability and create conditions for decisive action. Success in deception is not based on what friendly forces do, but by what the enemy demonstrates they believe, measured by the actions they take. When applied effectively, deception forces adversaries to waste resources, commit to false targets, and fight based on a reality that no longer ever existed.
By CPT Paul Dolan
Paul T. Dolan, a Captain in the Army, is currently assigned as a Battalion Intelligence Trainer with Panther Team at the National Training Center in Fort Irwin, California. Prior to this, he served as a Squadron Intelligence Trainer with Cobra Team, also at the National Training Center. Previous assignments include Battalion Intelligence Officer for 2-8 Cavalry, 1st Cavalry Division; Current Operations Intelligence Officer for Task Force South East in Paktia Province, Afghanistan; and Platoon Leader for Bravo Troop, 1-40 Cavalry, 4th Brigade Combat Team, 25th Infantry Division. His military schooling includes the Armor Basic Officer Leader Course at Fort Benning, Georgia; Stryker Leader Course at Fort Benning, Georgia; Military Intelligence Captains Career Course at Fort Huachuca, Arizona; and the Army Space Basic Cadre Course at Peterson Space Force Base, Colorado. Dolan holds a Bachelor of Arts in Studies in War and Peace from Norwich University and is currently pursuing a Master of Science in Unmanned and Autonomous Systems from Embry Riddle Aeronautical University.
Notes
1 ATP 7-100.1, “Russian Tactics”, 2024
2FM 3-90, “Tactics”, 2019
3ATP 7-100.1, “Russian Tactics”, 2024
4 ATP 7-100.2, “North Korean Tactics”, 2024
5 FM 3-90, “Tactics”, 2019
6 ATP 6-02.53, “Techniques for Tactical Radio Operations”, 2019
7 FM 3-90, “Tactics”, 2019
































































































































