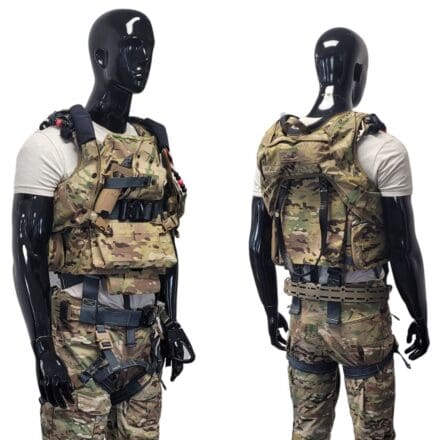
FORT LIBERTY, N.C. — Airborne and special forces Soldiers at Fort Liberty are testing the latest small arms weapon sights.
The 82nd Airborne Division, joined by the 3rd and 10th Special Forces Groups, are in the final stages of testing the Family of Weapons Sights – Individual, or FWS-I, for static line and military free fall airborne infiltration.
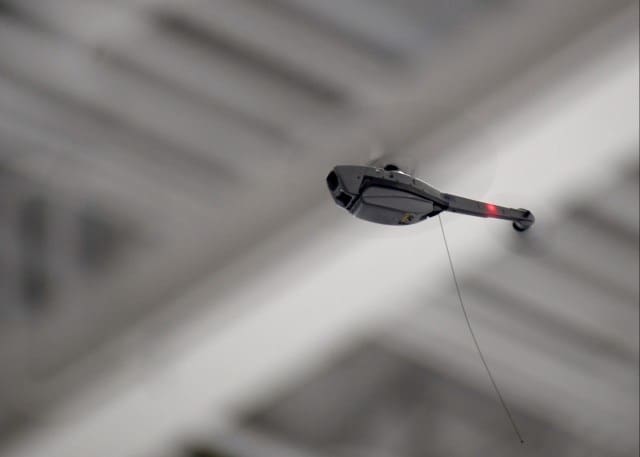
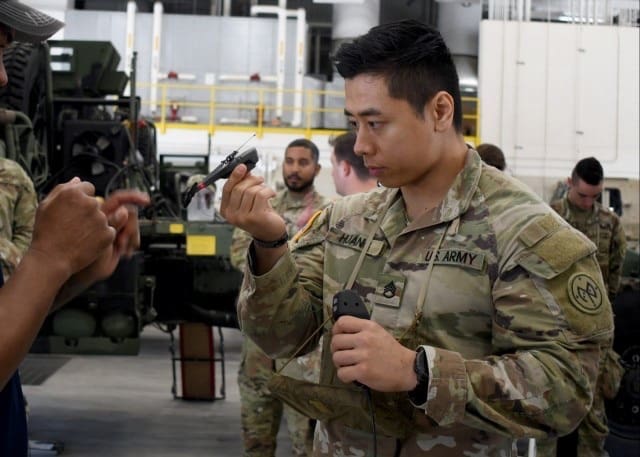
The FWS-I program will provide Soldiers with thermal enablers for individual weapons.
“The FWS-I gives Soldiers the capability to see farther into the battlefield, increase surveillance and target acquisition range, and penetrate day or night obscurants,” said Lashon Wilson, a test coordinator for Project Manager Soldier Lethality.
“American paratroopers and special operations Soldiers are renowned for attacking when and where least expected and almost exclusively at night,” said Staff Sgt. Derek Pattle a test NCO with the Airborne and Special Operations Test Directorate, also known as ABNSOTD.

“Conducting forced entry operations during daylight hours leaves paratroopers exposed to enemy ground fire and counterattack during airborne assault,” he added.
“That’s why mastering night vision devices and targeting systems is a critical skill for Army paratroopers and Special Operators and vital to mission accomplishment during forced entry parachute assault.”
According to Capt. Joseph Chabries, a plans officer at ABNSOTD, the core question for military equipment employed by Army paratroopers and special operations regarding is in its survivability.
“’Can the system survive airborne infiltration?’” said Chabries.
“Individual paratroopers as well as vehicles and cargo delivery systems are bristling with technology, which can at times be fragile,” he added.
“Ensuring these systems are both suitable and effective for issue to airborne forces often requires a more technical approach.”

Staff Sgt. Dalton Carter, a weapons squad leader with 2nd Brigade, 82nd Airborne Division said, “I feel as if this is a step in the right direction for army night vision and lauded the operational features the FWS-I can provide his squad.”
The FWS-I test also exposed many veteran paratroopers to operational testing for the first time.
Sgt. David Brown, a fire team leader in Bravo Company, 1-325 Airborne Infantry Regiment, serving as a test participant during static line testing, said, “I feel like the FWS-I can be a real force multiplier for key leaders during hours of limited visibility or when the battlefield might be obscured.”
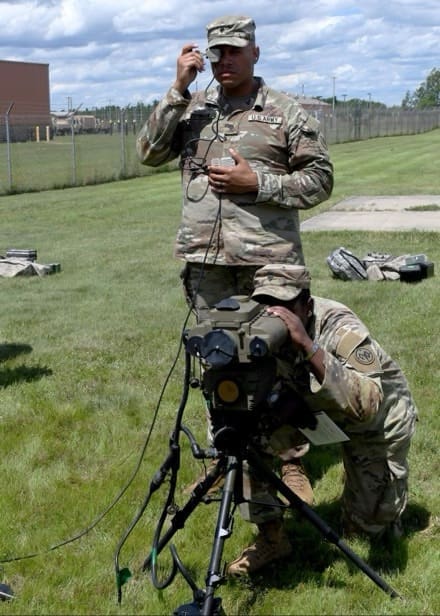
During post-drop operations, jumpers assembled for accountability and to ensure all FWS-Is were fully mission capable by performing a system functions check and collimation using the mobile boresight collimation station, which is used to evaluate the bore sight retention and repeatability of the FWS-I before and after static line and military free fall infiltration.

The data from the mobile boresight collimation station allows the test team to determine if and how much the boresight reticle on the FWS-I was moved or displaced due to any shock induced from exiting the aircraft, the opening of the parachute canopy or landing on the ground.
“ABNSOTD is one of the few organizations in the Department of Defense that maintains a bore sight collimation capability and the only mobile system of its kind,” said Mr. Jacob Boll, ABNSOTD’s operational research analyst.
The ABNSOTD instrumentation section is charged with maintaining and employing this unique capability and trained extensively to conduct post-drop weapons testing before beginning operational testing of FWS-I.
Maj. Joshua Cook, deputy chief of ABNSOTD’s Test Division described the importance of testing and how it plays into the future of technology in warfare.
“Operational testing is about Soldiers and ensuring the systems developed are effective in a Soldier’s hands and suitable for the environments in which they train and fight,” Cook said.
By Mr. Mike Shelton, Test Officer, Airborne and Special Operations Test Directorate, U.S. Army Operational Test Command