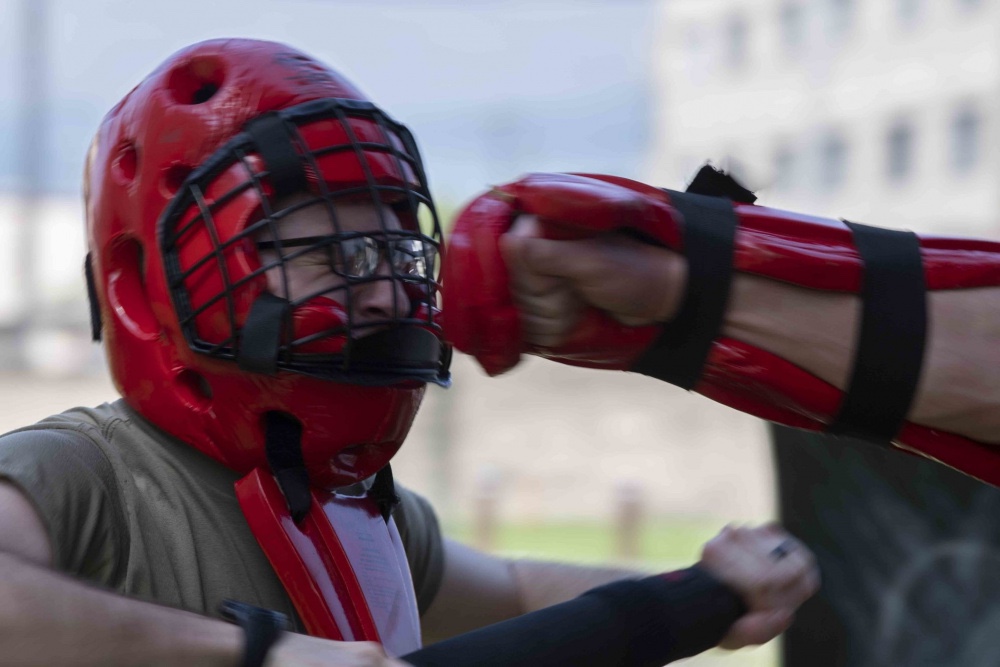
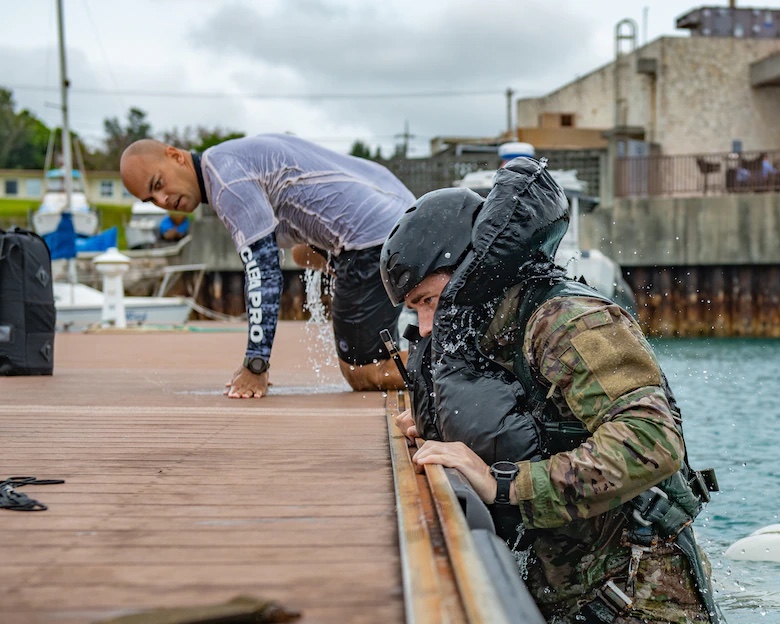
JOINT BASE SAN ANTONIO-CHAPMAN TRAINING ANNEX, Texas—The Special Warfare Human Performance Squadron, SWHPS, recently marked its second anniversary.

The SWHPS is the first squadron of its kind in the Department of Defense, and its sole purpose is to provide Special Warfare Airmen and cadre embedded/holistic Human Performance, HP support.

“We reached our two-year milestone as a squadron and I cannot tell you how immensely proud I am of the team,” said Lt. Col. Shawnee A. Williams, SWHPS, commander. “With all of the hard work done to stand up the SWHPS, I am excited to see this capability propel forward every day!”

The SWHPS mission statement is to optimize the performance, durability, and sustainability of the Special Warfare human weapon system by taking an interdisciplinary approach toward the advancement of science and technology throughout the SW operator’s lifespan.

The organizational structure is made up of five geographically separated units, GSU, across the United States coast-to-coast. Within this construct are nine human performance flights supporting 80 Special Warfare cadre, 500 support staff, and 1,100 Special Warfare students annually.
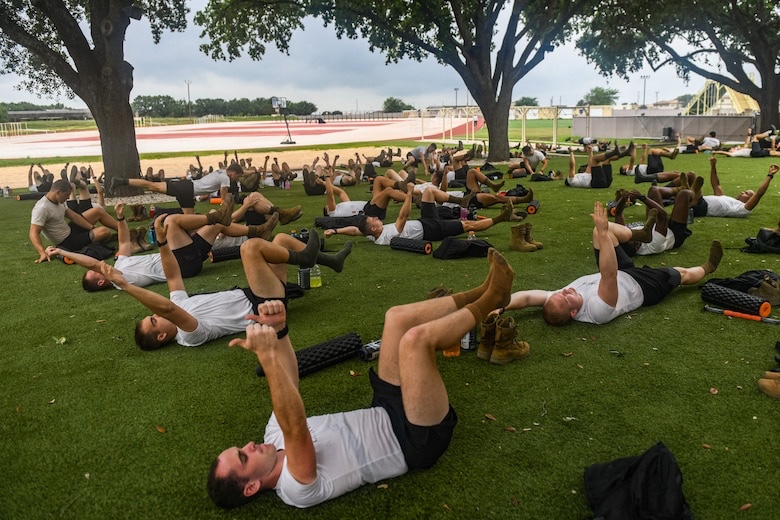

“Our team sets the foundation for building physically superior, mentally sharper, and spiritually stronger warriors who will go into harm’s way to tackle our nation’s most dangerous and difficult tasks,” said Col. George Buse, Special Warfare Human Performance Support Group, commander. “To this end, SWHPS focuses on being brilliant at instilling HP principles in SW Airmen. We also leverage technological advances, research capabilities, and a holistic approach for the sake of further integrating and professionalizing the SW training enterprise,” said Buse.
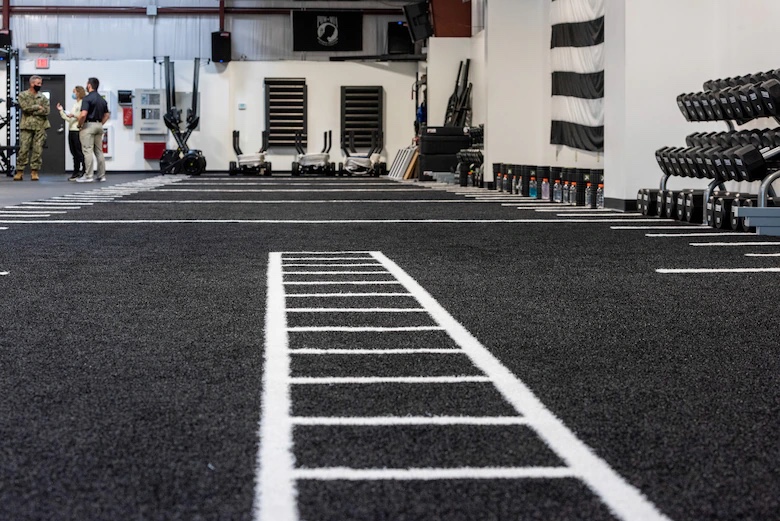

Some key accomplishments of the SWHPS include standing up the first SW Human Performance purpose-built facility and hence named the Airman 1st Class Baker Combat Conditioning Center at the Panama City Dive School, Panama City, Florida. This facility occupies 13K square feet, $1.3 million in performance equipment, and serves a joint population of cadre and students with over 700K annual course hours.
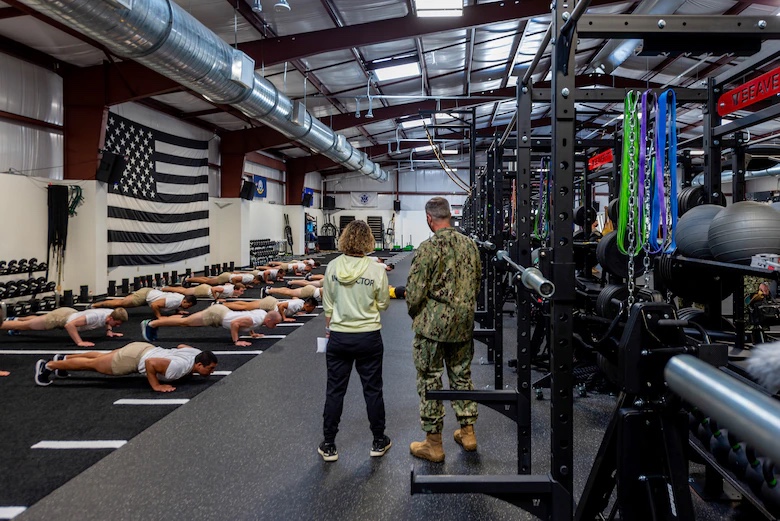

At GSU location Yuma, Arizona, the first-ever embedded physical therapist for Army and Air Force personnel position has been established to increase access to care for evaluation, diagnosis, treatment, and injury prevention services for trainees and support staff members at Military Free Fall Courses.
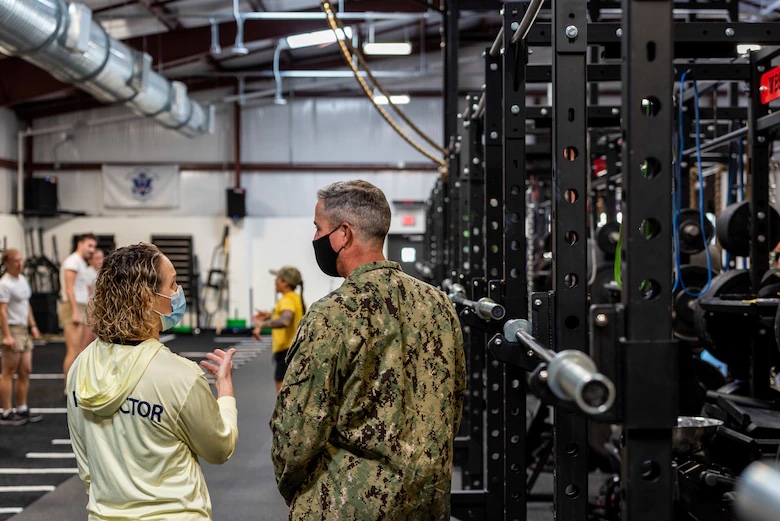

Educationally, SWHPS has established a location at the U.S. Air Force Academy and took on their USAF Physical Therapy Fellowship Program for the Air Force Medical Service, and propelled it forward (was not under the old Battle Field Airmen Model). The Fellowship program has since graduated eight fellows with three more due to graduate in 2021 and has secured national accreditation.

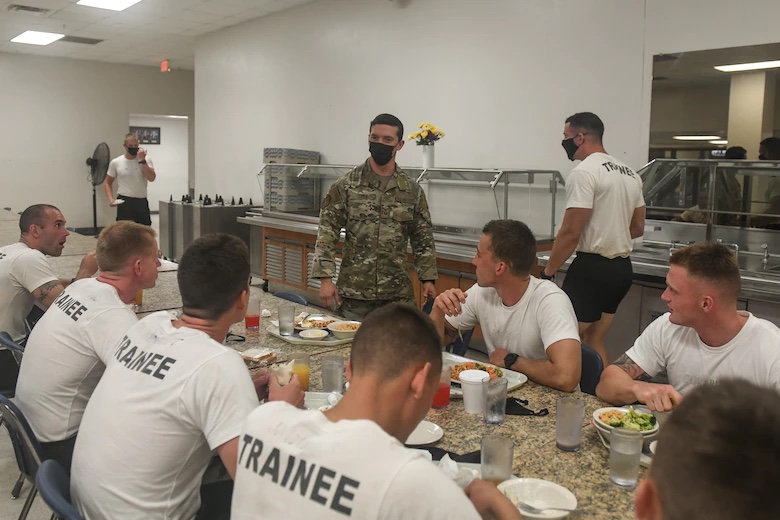
Additionally, SWHPS has established a human performance footprint, across the training pipeline that employs integrated wearable technology, along with HP technician support. This footprint enables SWHPS to track parasympathetic/sympathetic system output, sleep, musculoskeletal health, velocity-based training, and water-based event metrics to include heart rate and physiological data points.
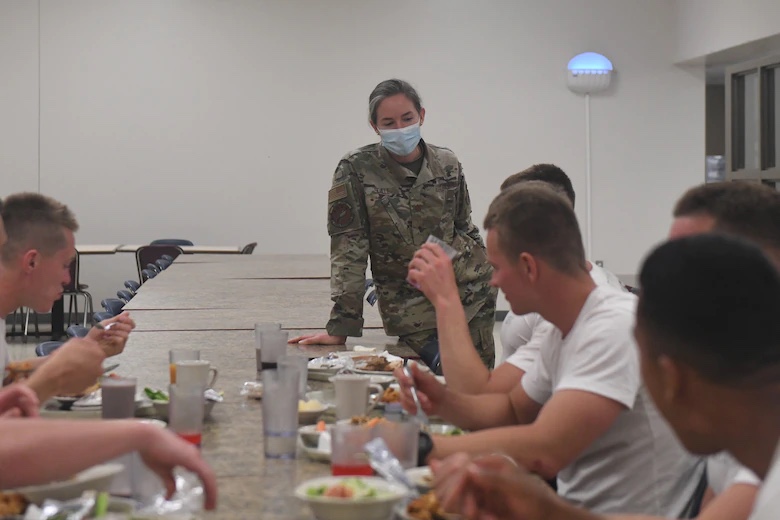

“Another first of its kind is the HP portfolio integration with the Learning Management System/database. The integration will soon provide continuity between training and operational units,” Williams said. “This allows for a human performance portfolio to travel with each member throughout their Special Warfare career.”

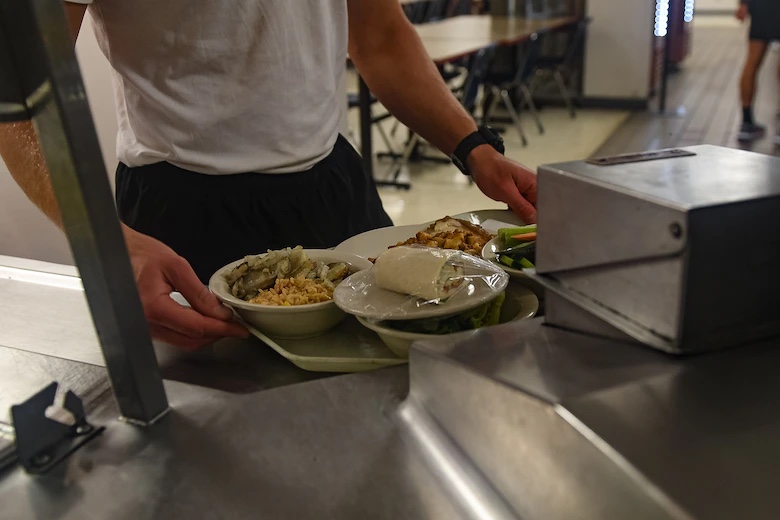
The Squadron’s Nutrition SMEs created the first stand-alone performance dining facility and now oversee all menus in support of the Special Warfare Preparatory Program. “It provides a much-needed ‘learning lab for trainees when they first enter Special Warfare,” said Maj. Miriam Seville, the lead dietitian for the Special Warfare Training Wing. “The trainees get to practice the sports nutrition principles that they learn in class and experiment with a wide variety of healthful foods and beverages that fuel and sustain optimal performance.
“This dining facility introduces trainees to what fueling the Human Weapon System can and should look like, and enables them to build habits here that will support them throughout their training and into operational status,” she said.
In November of 2020, the SWHPS graduated the first Air Force Institute of Technology Performance Nutrition Fellow, who now brings world-class nutrition capability, guidance, and knowledge to Special Warfare programming.
Williams added a final thought on the accomplishments of the program, “Over the past two years, SWHPS has set the foundation for an integrated approach to building and maintaining a human weapon system. We have taken a purposeful and tailored approach to embedded HP and coupled it with real-time physiological feedback to the trainees and are also expanding care to the cadre,” she said.
“The future of this organization will be to shape not only Air Force, but DOD policy to enable a lifecycle platform for the SW operator. The SW Airmen will not just experience high-level/holistic HP support in the training pipeline, but rather, they will see it woven into their career field education and training plans, and expanded services offered in their operational units,” she said. “This then lends itself to the creation or standup of a human weapon system program office just like we have for our hardware.
“We are truly on the cusp of a cohesive training environment where physiological, cognitive, and resiliency elements are assessed weekly, if not daily, to propel the individual to their highest potential versus a binary reactive environment,” Williams concluded.
Members of the Special Warfare Training Wing provide initial training for all U.S. Air Force Special Warfare training AFSCs, to include, Combat Controllers, Pararescue, Special Reconnaissance, and Tactical Air Control Party Airmen.
To learn more about SR Airmen or other U.S. Air Force Special Warfare career opportunities, go to: www.airforce.com/careers/in-demand-careers/special-warfare.
By Andrew C. Patterson, Special Warfare Training Wing/ Public Affairs